Hepatitis C in Hemodialysis Units: diagnosis and therapeutic approach
- PMID: 30806444
- PMCID: PMC6979573
- DOI: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2018-0177
Hepatitis C in Hemodialysis Units: diagnosis and therapeutic approach
Abstract
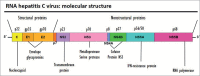
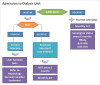
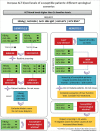
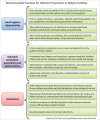
According to data from the last census of the Brazilian Society of Nephrology (SBN), the prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in Brazilian hemodialysis units (HU) is 3.3%, about three times higher than what is reported for the Brazilian general population. Often, professionals working in HU are faced with clinical situations that require rapid HCV diagnosis in order to avoid horizontal transmission within the units. On the other hand, thanks to the development of new antiviral drugs, the cure of patients with HCV, both in the general population and in patients with chronic kidney disease and the disease eradication, appear to be very feasible objectives to be achieved in the near future . In this scenario, SBN and the Brazilian Society of Hepatology present in this review article a proposal to approach HCV within HUs.
De acordo com os dados do último censo da Sociedade Brasileira de Nefrologia (SBN), a prevalência de portadores do vírus da hepatite C (HCV) nas unidades de hemodiálise (UH) no Brasil é de 3,3%, cerca de três vezes maior do que é observado na população geral brasileira. Muitas vezes, os profissionais que trabalham nas UH deparam-se com situações clínicas que demandam rápido diagnóstico do HCV, a fim de evitar uma transmissão horizontal dentro das unidades. Por outro lado, a cura dos pacientes portadores do HCV, tanto na população geral como na portadora de doença renal crônica e a erradicação da doença, em virtude do desenvolvimento de novas drogas antivirais, parecem ser objetivos bastante factíveis, a ser alcançados em futuro próximo. Nesse cenário, a SBN e a Sociedade Brasileira de Hepatologia apresentam neste artigo de revisão uma proposta de abordagem do HCV dentro das UH.
Figures
References
-
- Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Mohd Hanafiah K, Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age-specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology. 2013;57:1333–1342. - PubMed
-
- Gower E, Estes C, Blach S, Razavi-Shearer K, Razavi H. Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 2014;61:S45–S57. - PubMed
-
- Fissell RB, Bragg-Gresham JL, Woods JD, Jadoul M, Gillespie B, Hedderwick SA, et al. Patterns of hepatitis C prevalence and seroconversion in hemodialysis units from three continents: the DOPPS. Kidney Int. 2004;65:2335–2342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

