Association of Overlapping Surgery With Perioperative Outcomes
- PMID: 30806696
- PMCID: PMC6439866
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2019.0711
Association of Overlapping Surgery With Perioperative Outcomes
Abstract
Importance: Overlapping surgery, in which more than 1 procedure performed by the same primary surgeon is scheduled so the start time of one procedure overlaps with the end time of another, is of concern because of potential adverse outcomes.
Objective: To determine the association between overlapping surgery and mortality, complications, and length of surgery.
Design, setting, and participants: Retrospective cohort study of 66 430 operations in patients aged 18 to 90 years undergoing total knee or hip arthroplasty; spine surgery; coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery; and craniotomy at 8 centers between January 1, 2010, and May 31, 2018. Patients were followed up until discharge.
Exposures: Overlapping surgery (≥2 operations performed by the same surgeon in which ≥1 hour of 1 case, or the entire case for those <1 hour, occurs when another procedure is being performed).
Main outcomes and measures: Primary outcomes were in-hospital mortality or complications (major: thromboembolic event, pneumonia, sepsis, stroke, or myocardial infarction; minor: urinary tract or surgical site infection) and surgery duration.
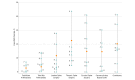
Results: The final sample consisted of 66 430 operations (mean patient age, 59 [SD, 15] years; 31 915 women [48%]), of which 8224 (12%) were overlapping. After adjusting for confounders, overlapping surgery was not associated with a significant difference in in-hospital mortality (1.9% overlapping vs 1.6% nonoverlapping; difference, 0.3% [95% CI, -0.2% to 0.7%]; P = .21) or risk of complications (12.8% overlapping vs 11.8% nonoverlapping; difference, 0.9% [95% CI, -0.1% to 1.9%]; P = .08). Overlapping surgery was associated with increased surgery length (204 vs 173 minutes; difference, 30 minutes [95% CI, 24 to 37 minutes]; P < .001). Overlapping surgery was significantly associated with increased mortality and increased complications among patients having a high preoperative predicted risk for mortality and complications, compared with low-risk patients (mortality: 5.8% vs 4.7%; difference, 1.2% [95% CI, 0.1% to 2.2%]; P = .03; complications: 29.2% vs 27.0%; difference, 2.3% [95% CI, 0.3% to 4.3%]; P = .03).
Conclusions and relevance: Among adults undergoing common operations, overlapping surgery was not significantly associated with differences in in-hospital mortality or postoperative complication rates but was significantly associated with increased surgery length. Further research is needed to understand the association of overlapping surgery with these outcomes among specific patient subgroups.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Overlapping Surgery and Perioperative Outcomes.JAMA. 2019 Feb 26;321(8):772. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.1123. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 30806675 No abstract available.
-
Re: Association of Overlapping Surgery with Perioperative Outcomes.J Urol. 2019 Aug;202(2):200. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000322. Epub 2019 Jul 8. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31063071 No abstract available.
-
Outcomes Associated With Overlapping Surgery.JAMA. 2019 Jul 16;322(3):274. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.6459. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31310291 No abstract available.
-
Outcomes Associated With Overlapping Surgery.JAMA. 2019 Jul 16;322(3):274-275. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.6463. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31310292 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American College of Surgeons (ACS) Statements on Principles. ACS website. https://www.facs.org/about-acs/statements/stonprin. Revised April 12, 2016. Accessed December 28, 2018.
-
- Abelson J, Saltzman J, Kowalczyk L, Allen S Clash in the name of care. Boston Globe October 25, 2015. https://apps.bostonglobe.com/spotlight/clash-in-the-name-of-care/story/. Accessed January 28, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

