Molecular characterization of Histomonas meleagridis exoproteome with emphasis on protease secretion and parasite-bacteria interaction
- PMID: 30807611
- PMCID: PMC6391000
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212429
Molecular characterization of Histomonas meleagridis exoproteome with emphasis on protease secretion and parasite-bacteria interaction
Abstract
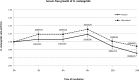
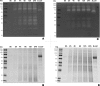
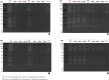
The exoproteome of parasitic protists constitutes extracellular proteins that play a fundamental role in host-parasite interactions. Lytic factors, especially secreted proteases, are capable of modulating tissue invasion, thereby aggravating host susceptibility. Despite the important role of exoproteins during infection, the exoproteomic data on Histomonas meleagridis are non-existent. The present study employed traditional 1D-in-gel-zymography (1D-IGZ) and micro-LC-ESI-MS/MS (shotgun proteomics), to investigate H. meleagridis exoproteomes, obtained from a clonal virulent and an attenuated strain. Both strains were maintained as mono-eukaryotic monoxenic cultures with Escherichia coli. We demonstrated active in vitro secretion kinetics of proteases by both parasite strains, with a widespread proteolytic activity ranging from 17 kDa to 120 kDa. Based on protease inhibitor susceptibility assay, the majority of proteases present in both exoproteomes belonged to the family of cysteine proteases and showed stronger activity in the exoproteome of a virulent H. meleagridis. Shotgun proteomics, aided by customized database search, identified 176 proteins including actin, potential moonlighting glycolytic enzymes, lytic molecules such as pore-forming proteins (PFPs) and proteases like cathepsin-L like cysteine protease. To quantify the exoproteomic differences between the virulent and the attenuated H. meleagridis cultures, a sequential window acquisition of all theoretical spectra mass spectrometric (SWATH-MS) approach was applied. Surprisingly, results showed most of the exoproteomic differences to be of bacterial origin, especially targeting metabolism and locomotion. By deciphering such molecular signatures, novel insights into a complex in vitro protozoan- bacteria relationship were elucidated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host-specific targets of Histomonas meleagridis antigens revealed by immunoprecipitation.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88855-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962091 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the differences: comparative proteomic analysis of a clonal virulent and an attenuated Histomonas meleagridis strain.Int J Parasitol. 2018 Feb;48(2):145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2017.08.017. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Int J Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29203214
-
An Alliance of Gel-Based and Gel-Free Proteomic Techniques Displays Substantial Insight Into the Proteome of a Virulent and an Attenuated Histomonas meleagridis Strain.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Nov 16;8:407. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00407. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30505807 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the Immunity of Poultry Against the Extracellular Protozoan Parasite Histomonas meleagridis Is a Cornerstone for Vaccine Development: A Review.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 2;9:2518. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02518. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30450097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Histomonas meleagridis and Bacteria: Mutualistic or Predator-Prey?Trends Parasitol. 2020 Mar;36(3):232-235. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2019.12.015. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Trends Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 31982329 Review.
Cited by
-
Histomonosis in Poultry: A Comprehensive Review.Front Vet Sci. 2022 May 6;9:880738. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.880738. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35601402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Profile of Histomonas meleagridis in Dwyer's Media with and Without Rice Starch.Metabolites. 2024 Nov 22;14(12):650. doi: 10.3390/metabo14120650. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39728431 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genomes of the eukaryotic poultry parasite Histomonas meleagridis: linking sequence analysis with virulence / attenuation.BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 21;22(1):753. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08059-2. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34674644 Free PMC article.
-
Host-specific targets of Histomonas meleagridis antigens revealed by immunoprecipitation.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88855-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962091 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Surfaceome Analysis of Clonal Histomonas meleagridis Strains with Different Pathogenicity Reveals Strain-Dependent Profiles.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 21;10(10):1884. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101884. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296163 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

