Myosin-X Silencing in the Trabecular Meshwork Suggests a Role for Tunneling Nanotubes in Outflow Regulation
- PMID: 30807639
- PMCID: PMC6390986
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.18-26055
Myosin-X Silencing in the Trabecular Meshwork Suggests a Role for Tunneling Nanotubes in Outflow Regulation
Abstract
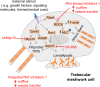
Purpose: The actin cytoskeleton plays a key role in outflow regulation through the trabecular meshwork (TM). Although actin stress fibers are a target of glaucoma therapies, the role of other actin cellular structures is unclear. Myosin-X (Myo10) is an actin-binding protein that is involved in tunneling nanotube (TNT) and filopodia formation. Here, we inhibited Myo10 pharmacologically or by gene silencing to investigate the role of filopodia/TNTs in the TM.
Methods: Short hairpin RNA interference (RNAi) silencing lentivirus targeting myosin-X (shMyo10) was generated. Human anterior segments were perfused with shMyo10 or CK-666, an Arp2/3 inhibitor. Confocal microscopy investigated the colocalization of Myo10 with matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs). Western immunoblotting investigated the protein levels of MMPs and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. MMP activity and phagocytosis assays were performed.
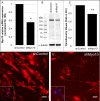
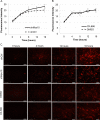
Results: CK-666 and shMyo10-silencing lentivirus caused a significant reduction in outflow rates in anterior segment perfusion culture, an ex vivo method to study intraocular pressure regulation. In human TM cells, Myo10 colocalized with MMP2, MMP14, and cortactin in podosome-like structures, which function as regions of focal ECM degradation. Furthermore, MMP activity, thrombospondin-1 and SPARC protein levels were significantly reduced in the media of CK-666-treated and shMyo10-silenced TM cells. However, neither Myo10 silencing or CK-666 treatment significantly affected phagocytic uptake.
Conclusions: Inhibiting filopodia/TNTs caused opposite effects on outflow compared with inhibiting stress fibers. Moreover, Myo10 may also play a role in focal ECM degradation in TM cells. Our results provide additional insight into the function of actin supramolecular assemblies and actin-binding proteins in outflow regulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential effects of caveolin-1 and -2 knockdown on aqueous outflow and altered extracellular matrix turnover in caveolin-silenced trabecular meshwork cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Aug 7;55(9):5497-509. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14519. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 25103269 Free PMC article.
-
Tunneling Nanotubes are Novel Cellular Structures That Communicate Signals Between Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Oct 1;58(12):5298-5307. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22732. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 29049733 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Functional Alterations in Tunneling Nanotubes Formed by Glaucomatous Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Nov 1;60(14):4583-4595. doi: 10.1167/iovs.19-28084. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31675075 Free PMC article.
-
Pressure-induced expression changes in segmental flow regions of the human trabecular meshwork.Exp Eye Res. 2017 May;158:67-72. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Jun 19. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27334250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular matrix in the trabecular meshwork: intraocular pressure regulation and dysregulation in glaucoma.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Apr;133:112-25. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.07.014. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25819459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Normal and glaucomatous outflow regulation.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021 May;82:100897. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100897. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 32795516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Retinal Tissue in an S100B Autoimmune Glaucoma Model.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 23;11(1):16. doi: 10.3390/biology11010016. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35053014 Free PMC article.
-
Tunneling Nanotube: An Enticing Cell-Cell Communication in the Nervous System.Biology (Basel). 2023 Sep 27;12(10):1288. doi: 10.3390/biology12101288. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37886998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Mechanical Stretch on Integrins and Filopodial-Associated Proteins in Normal and Glaucomatous Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 29;10:886706. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.886706. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573666 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of cholesterol in modulating actin dynamics and cell adhesive interactions in the trabecular meshwork.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 4:2024.02.02.578717. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.02.578717. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38352310 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Quigley HA. Glaucoma. Lancet. 2011;377:1367–1377. - PubMed
-
- Nobes CD, Rho Hall A. rac and cdc42 GTPases: regulators of actin structures, cell adhesion and motility. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995;23:456–459. - PubMed
-
- Rao PV, Deng PF, Kumar J, Epstein DL. Modulation of aqueous humor outflow facility by the Rho kinase-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:1029–1037. - PubMed
-
- Vittitow JL, Garg R, Rowlette LL, Epstein DL, O'Brien ET, Borras T. Gene transfer of dominant-negative RhoA increases outflow facility in perfused human anterior segment cultures. Mol Vis. 2002;8:32–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

