The role of dePARylation in DNA damage repair and cancer suppression
- PMID: 30807923
- PMCID: PMC7406231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.02.002
The role of dePARylation in DNA damage repair and cancer suppression
Abstract
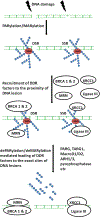
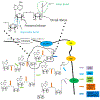
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PARylation) is a reversible post-translational modification regulating various biological pathways including DNA damage repair (DDR). Rapid turnover of PARylation is critically important for an optimal DNA damage response and maintaining genomic stability. Recent studies show that PARylation is tightly regulated by a group of enzymes that can erase the ADP-ribose (ADPR) groups from target proteins. The aim of this review is to present a comprehensive understanding of dePARylation enzymes, their substrates and roles in DDR. Special attention will be laid on the role of these proteins in the development of cancer and their feasibility in anticancer therapeutics.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functions of PARylation in DNA Damage Repair Pathways.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.001. Epub 2016 May 27. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27240471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting dePARylation in cancer therapy.DNA Repair (Amst). 2025 Apr;148:103824. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2025.103824. Epub 2025 Mar 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40056493 Review.
-
Poly-ADP ribosylation in DNA damage response and cancer therapy.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;780:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31395352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose): PARadigms and PARadoxes.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1046-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.010. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23290998 Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in carcinogenesis.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1202-16. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 25. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23714734 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular basis for the MacroD1-mediated hydrolysis of ADP-ribosylation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Oct;94:102899. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102899. Epub 2020 Jun 22. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32683309 Free PMC article.
-
Selective small molecule PARG inhibitor causes replication fork stalling and cancer cell death.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 11;10(1):5654. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13508-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31827085 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting dePARylation for cancer therapy.Cell Biosci. 2020 Jan 29;10:7. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-0375-y. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32010441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Truncated PARP1 mediates ADP-ribosylation of RNA polymerase III for apoptosis.Cell Discov. 2022 Jan 18;8(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41421-021-00355-1. Cell Discov. 2022. PMID: 35039483 Free PMC article.
-
PARG inhibitor sensitivity correlates with accumulation of single-stranded DNA gaps in preclinical models of ovarian cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 19;121(47):e2413954121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413954121. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39546575 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

