Transcriptome analysis of air-breathing land slug, Incilaria fruhstorferi reveals functional insights into growth, immunity, and reproduction
- PMID: 30808280
- PMCID: PMC6390351
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-019-5526-3
Transcriptome analysis of air-breathing land slug, Incilaria fruhstorferi reveals functional insights into growth, immunity, and reproduction
Abstract
Background: Incilaria (= Meghimatium) fruhstorferi is an air-breathing land slug found in restricted habitats of Japan, Taiwan and selected provinces of South Korea (Jeju, Chuncheon, Busan, and Deokjeokdo). The species is on a decline due to depletion of forest cover, predation by natural enemies, and collection. To facilitate the conservation of the species, it is important to decide on a number of traits related to growth, immunity and reproduction addressing fitness advantage of the species.
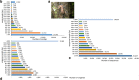
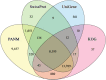
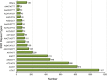
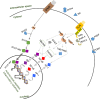
Results: The visceral mass transcriptome of I. fruhstorferi was enabled using the Illumina HiSeq 4000 sequencing platform. According to BUSCO (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs) method, the transcriptome was considered complete with 91.8% of ortholog genes present (Single: 70.7%; Duplicated: 21.1%). A total of 96.79% of the raw read sequences were processed as clean reads. TransDecoder identified 197,271 contigs that contained candidate-coding regions. Of a total of 50,230 unigenes, 34,470 (68.62% of the total unigenes) annotated to homologous proteins in the Protostome database (PANM-DB). The GO term and KEGG pathway analysis indicated genes involved in metabolism, phosphatidylinositol signalling system, aminobenzoate degradation, and T-cell receptor signalling pathway. Many genes associated with molluscan innate immunity were categorized under pathogen recognition receptor, TLR signalling pathway, MyD88 dependent pathway, endogenous ligands, immune effectors, antimicrobial peptides, apoptosis, and adaptation-related. The reproduction-associated unigenes showed homology to protein fem-1, spermatogenesis-associated protein, sperm associated antigen, and testis expressed sequences, among others. In addition, we identified key growth-related genes categorized under somatotrophic axis, muscle growth, chitinases and collagens. A total of 4822 Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) were also identified from the unigene sequences of I. fruhstorferi.
Conclusions: This is the first available genomic information for non-model land slug, I. fruhstorferi focusing on genes related to growth, immunity, and reproduction, with additional focus on microsatellites and repeating elements. The transcriptome provides access to greater number of traits of unknown relevance in the species that could be exploited for in-depth analyses of evolutionary plasticity and making informed choices during conservation planning. This would be appropriate for understanding the dynamics of the species on a priority basis considering the ecological, health, and social benefits.
Keywords: Immunity; Incilaria fruhstorferi; Peptidoglycan recognition protein; Sex-linked genes; Simple sequence repeats; Tollip; Transciptome; de novo analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No permission was required for the collection of slugs in this study. Further, this study was approved by Soonchunhyang University, South Korea. This study was conducted in accordance to the ethical guidelines for use of experimental animals in biomedical research.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis of the endangered dung beetle Copris tripartitus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) and characterization of genes associated to immunity, growth, and reproduction.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 2;24(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09122-w. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36864388 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and de novo assembly of visceral mass transcriptome of the critically endangered land snail Satsuma myomphala: Annotation and SSR discovery.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Mar;21:77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28107688
-
Sequencing, De Novo Assembly, and Annotation of the Transcriptome of the Endangered Freshwater Pearl Bivalve, Cristaria plicata, Provides Novel Insights into Functional Genes and Marker Discovery.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 12;11(2):e0148622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148622. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26872384 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the endangered mollusks transcriptome under the threatened species initiative of Korea.Genes Genomics. 2023 Aug;45(8):969-987. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01389-3. Epub 2023 Jul 5. Genes Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37405596 Review.
-
Examining adaptive evolution of immune activity: opportunities provided by gastropods in the age of 'omics'.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021 May 24;376(1825):20200158. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0158. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33813886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
De novo genome assembly and transcriptome sequencing in foot and mantle tissues of Megaustenia siamensis reveals components of adhesive substances.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 14;14(1):13756. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64425-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38877053 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of the endangered dung beetle Copris tripartitus (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) and characterization of genes associated to immunity, growth, and reproduction.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 2;24(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09122-w. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36864388 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-Related Gene Profiles and Differential Expression in the Grey Garden Slug Deroceras reticulatum Infected with the Parasitic Nematode Phasmarhabditis hermaphrodita.Insects. 2024 Apr 26;15(5):311. doi: 10.3390/insects15050311. Insects. 2024. PMID: 38786867 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of MiRNA Transcriptome in Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) Intestine Following Vibrio anguillarum Infection.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2019 Aug;21(4):550-564. doi: 10.1007/s10126-019-09903-z. Epub 2019 May 21. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2019. PMID: 31111338
References
-
- Collinge WE. Description of some new species of slug collected by Mr. H Fruhstofer J Malacol. 1901;8:118–121.
-
- Noseworthy RG, Lim NR, Choi KS. A catalogue of the mollusks of Jeju Island, South Korea. Kor J Malacol. 2007;23:65–104.
-
- Yuasa HJ, Furuta E, Nakamura A, Takagi T. Cloning and sequencing of three C-type lectins from body surface mucus of the land slug, Incilaria fruhstorferi. Comp Biochem Physiol B, Comp Biochem. 1998;119:479–484. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Chiarri M, Warren WC, Guo X, Proestou D. Developing tools for the study of molluscan immunity: the sequencing of the genome of the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Fish shellfish Immunol. 2015;46: 2-4.6. Raghavan N, Knight M. The snail (Biomphalaria glabrata) genome project. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:148–151. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

