Stem cells: past, present, and future
- PMID: 30808416
- PMCID: PMC6390367
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-019-1165-5
Stem cells: past, present, and future
Abstract
In recent years, stem cell therapy has become a very promising and advanced scientific research topic. The development of treatment methods has evoked great expectations. This paper is a review focused on the discovery of different stem cells and the potential therapies based on these cells. The genesis of stem cells is followed by laboratory steps of controlled stem cell culturing and derivation. Quality control and teratoma formation assays are important procedures in assessing the properties of the stem cells tested. Derivation methods and the utilization of culturing media are crucial to set proper environmental conditions for controlled differentiation. Among many types of stem tissue applications, the use of graphene scaffolds and the potential of extracellular vesicle-based therapies require attention due to their versatility. The review is summarized by challenges that stem cell therapy must overcome to be accepted worldwide. A wide variety of possibilities makes this cutting edge therapy a turning point in modern medicine, providing hope for untreatable diseases.
Keywords: Differentiation; Growth media; Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC); Pluripotency; Stem cell derivation; Stem cells; Teratoma formation assay; Tissue banks; Tissue transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
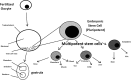
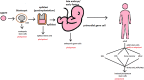
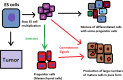
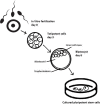
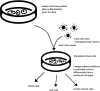

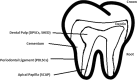
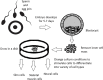
References
-
- Sukoyan MA, Vatolin SY, et al. Embryonic stem cells derived from morulae, inner cell mass, and blastocysts of mink: comparisons of their pluripotencies. Embryo Dev. 1993;36(2):148–58 - PubMed
-
- Larijani B, Esfahani EN, Amini P, Nikbin B, Alimoghaddam K, Amiri S, Malekzadeh R, Yazdi NM, Ghodsi M, Dowlati Y, Sahraian MA, Ghavamzadeh A. Stem cell therapy in treatment of different diseases. Acta Medica Iranica. 2012:79–96 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22359076. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan S, Stacey GN, Akazawa C, et al. Quality guidelines for clinical-grade human induced pluripotent stem cell lines. Regenerative Med. 2018; 10.2217/rme-2018-0095. - PubMed
-
- Amit M, Itskovitz-Eldor J. Atlas of human pluripotent stem cells: derivation and culturing. New York: Humana Press; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

