Consensus on the digestive endoscopic tunnel technique
- PMID: 30809078
- PMCID: PMC6385014
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.744
Consensus on the digestive endoscopic tunnel technique
Abstract
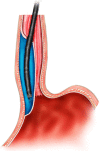
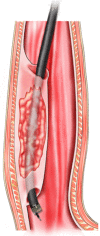
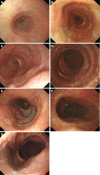
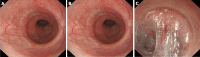
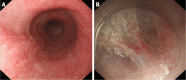
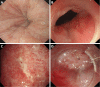
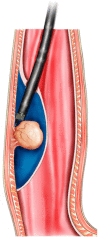
With the digestive endoscopic tunnel technique (DETT), many diseases that previously would have been treated by surgery are now endoscopically curable by establishing a submucosal tunnel between the mucosa and muscularis propria (MP). Through the tunnel, endoscopic diagnosis or treatment is performed for lesions in the mucosa, in the MP, and even outside the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. At present, the tunnel technique application range covers the following: (1) Treatment of lesions originating from the mucosal layer, e.g., endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection for oesophageal large or circular early-stage cancer or precancerosis; (2) treatment of lesions from the MP layer, per-oral endoscopic myotomy, submucosal tunnelling endoscopic resection, etc.; and (3) diagnosis and treatment of lesions outside the GI tract, such as resection of lymph nodes and benign tumour excision in the mediastinum or abdominal cavity. With the increasing number of DETTs performed worldwide, endoscopic tunnel therapeutics, which is based on DETT, has been gradually developed and optimized. However, there is not yet an expert consensus on DETT to regulate its indications, contraindications, surgical procedure, and postoperative treatment. The International DETT Alliance signed up this consensus to standardize the procedures of DETT. In this consensus, we describe the definition, mechanism, and significance of DETT, prevention of infection and concepts of DETT-associated complications, methods to establish a submucosal tunnel, and application of DETT for lesions in the mucosa, in the MP and outside the GI tract (indications and contraindications, procedures, pre- and postoperative treatments, effectiveness, complications and treatments, and a comparison between DETT and other operations).
Keywords: Digestive endoscopic tunnel technique; Endoscopic submucosal tunnel dissection; Gastrointestinal tract; Per-oral endoscopic myotomy; Submucosal tunnelling endoscopic resection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
Figures
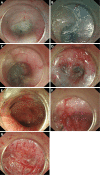
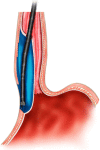
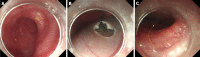
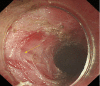

References
-
- Linghu E. Endoscopic resection for gastrointestinal pre-cancerous lesion and early cancer. Electronic Image Press of the Chinese Medical Association. 2009.
-
- Linghu E. Therapeutics of digestive endoscopic tunnel technique. Berlin: Springer; 2014. pp. 1–3.
-
- Linghu E. The establishment and prospect of endoscopic tunnel technique. Zhonghua Qiangjing Waike Zazhi (Electronic Edition) 2011;4:1–2.
-
- Linghu E. A view of the principle and base of endoscopic technique innovation from the development of endoscopic submucosa dissection and peroral endoscopic myotomy. Zhonghua Xiaohua Neijing Zazhi. 2011;28:603–604.
-
- Werner YB, Rösch T. POEM and Submucosal Tunneling. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2016;14:163–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

