Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it
- PMID: 30809079
- PMCID: PMC6385015
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777
Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it
Abstract
During the past decades, endoscopic resection techniques have gradually improved and gained more importance for the management of premalignant lesions and early cancers. These endoscopic resection techniques can be divided in 3 major groups: snare polipectomy, endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). The use of submucosal injection is essential for the majority of EMR techniques and is an integral part of ESD, whereas during polipectomy it is not crucial in most cases except to prevent bleeding in large polyps and/or those with large stalks as an alternative to mechanical methods. Injection provides a lifting up effect of the lesion separating it from the muscular layer, thereby reducing thermal injury and the risk of perforation and bleeding while also facilitating en-bloc resection by improving technical feasibility. With this work, we aim to review the most common endoscopic resection techniques and the importance of submucosal injection in each one of them. For that, we present some of the most commonly used submucosal injection solutions, taking into account their advantages and disadvantages. We also discuss, based on current recommendations and our own experience, how and when to preform submucosal injection, depending on lesions features and endoscopic resection technique that´s being used, to assure complete resection and to prevent associated adverse events. Finally, we also present and discuss some new proposed submucosal injection solutions, endoscopic resection techniques and devices that may have a major impact on the future of therapeutic endoscopy.
Keywords: Endoscopic mucosal resection; Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Snare polipectomy; Submucosal injection; Submucosal injection solution.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest. No financial support.
Figures
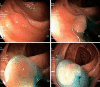
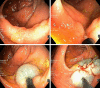

References
-
- Isomoto H. Global dissemination of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Intern Med. 2010;49:251–252. - PubMed
-
- Choi KS, Jung HY, Choi KD, Lee GH, Song HJ, Kim DH, Lee JH, Kim MY, Kim BS, Oh ST, Yook JH, Jang SJ, Yun SC, Kim SO, Kim JH. EMR versus gastrectomy for intramucosal gastric cancer: comparison of long-term outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73:942–948. - PubMed
-
- ASGE Technology Committee. Hwang JH, Konda V, Abu Dayyeh BK, Chauhan SS, Enestvedt BK, Fujii-Lau LL, Komanduri S, Maple JT, Murad FM, Pannala R, Thosani NC, Banerjee S. Endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;82:215–226. - PubMed
-
- Jung YS, Park DI. Submucosal injection solutions for endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal neoplasms. Gastrointest Inte. 2013;2:73–77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

