Paired Associative Electroacupuncture and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Humans
- PMID: 30809140
- PMCID: PMC6379477
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00049
Paired Associative Electroacupuncture and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Humans
Abstract
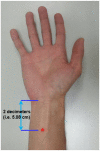
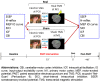
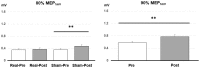
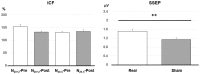
Pairing transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) with specific stimulus-intervals induces associative motor plasticity at the primary motor cortex (M1). Electroacupuncture (EA) is an established medical technique in the eastern countries. This study investigates whether EA paired with TMS induces distinct M1 motor plasticity. Fifteen healthy, right-handed subjects (aged 23.6 ± 2.0 years, eight women) were studied. Two-hundred and twenty-five pairs of TMS of the left M1 preceded by right EA at acupoint "Neiguan" [Pericardium 6 (PC6), located 2 decimeters proximal from the wrist wrinkle] were respectively applied with the interstimulus interval (ISI) of individual somatosensory evoked potential (SSEP) N20 latency plus 2 ms (N20+2) and minus 5 ms (N20-5) with at least 1-week interval. The paired stimulation was delivered at a rate of 0.25 Hz. Sham TMS with a sham coil was adopted to examine the low-frequency EA influence on M1 in eleven subjects. M1 excitability was assessed by motor-evoked potential (MEP) recruitment curve with five TMS intensity levels, short-interval intracortical inhibition (SICI), intracortical facilitation (ICF) and cerebellar inhibition (CBI) at the abductor pollicis brevis (APB) muscle of the right hand before and after the EA-M1 paired associative stimulation (PAS). In addition, median nerve SSEPs and H-reflex were respectively measured to monitor somatosensory and spinal excitability. The MEP showed significantly facilitated after the sham EA-M1 PAS while tested with 80% of the TMS intensity producing on average 1 mV amplitude (i.e., MEP1 mV) in the resting APB muscle. It was also facilitated while tested with 90% MEP1 mV irrespective of the stimulation conditions. The SSEP showed a higher amplitude from the real EA-M1 PAS compared to that from the sham EA-M1 PAS. No significant change was found on SICI, ICF, CBI and H-reflex. Findings suggest that repetitive low frequency EA paired with real TMS did not induce spike-timing dependent motor plasticity but EA paired with sham TMS induced specific M1 excitability change. Complex sensory afferents with dispersed time locked to the sensorimotor cortical area could hamper instead of enhancing the induction of the spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP) in M1.
Keywords: electroacupuncture; motor cortex; motor evoked potential; paired associative stimulation; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Convergent Associative Motor Cortical Plasticity Induced by Conditional Somatosensory and Motor Reaction Afferents.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Oct 21;14:576171. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.576171. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33192405 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellum to motor cortex paired associative stimulation induces bidirectional STDP-like plasticity in human motor cortex.Front Hum Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;6:260. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00260. eCollection 2012. Front Hum Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23049508 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Cerebellum to Primary Motor Cortex Associative Plasticity in Parkinson's Disease and Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3.Front Neurol. 2017 Aug 29;8:445. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00445. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28900413 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the connections between basal ganglia and cortex revealed by transcranial magnetic stimulation, evoked potential and deep brain stimulation in dystonia.Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2022 Jan;36:69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2021.12.004. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34922163 Review.
-
Non-invasive brain stimulation as a tool to study cerebellar-M1 interactions in humans.Cerebellum Ataxias. 2016 Nov 16;3:19. doi: 10.1186/s40673-016-0057-z. eCollection 2016. Cerebellum Ataxias. 2016. PMID: 27895926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in somatosensory evoked potentials elicited by lateral cerebellar nucleus deep brain stimulation in the naïve rodent.Neurosci Lett. 2022 Aug 24;786:136800. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136800. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Neurosci Lett. 2022. PMID: 35842210 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent Associative Motor Cortical Plasticity Induced by Conditional Somatosensory and Motor Reaction Afferents.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Oct 21;14:576171. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.576171. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33192405 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Interventions for Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Cognitive Disorders: A Review of Mechanisms.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 28;2022:6080282. doi: 10.1155/2022/6080282. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36211826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Hotspots and Effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Pain: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Jun 21;16:887246. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.887246. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35814960 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

