Computational Identification of Inhibitors Using QSAR Approach Against Nipah Virus
- PMID: 30809147
- PMCID: PMC6379726
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00071
Computational Identification of Inhibitors Using QSAR Approach Against Nipah Virus
Abstract
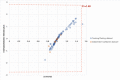
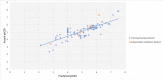
Nipah virus (NiV) caused several outbreaks in Asian countries including the latest one from Kerala state of India. There is no drug available against NiV till now, despite its urgent requirement. In the current study, we have provided a computational one-stop solution for NiV inhibitors. We have developed the first "anti-Nipah" web resource, which comprising of a data repository, prediction method, and data visualization module. The database contains of 313 (181 unique) chemicals extracted from research articles and patents, which were tested for different strains of NiV isolated from various outbreaks. Moreover, the quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) based regression predictors were developed using chemicals having half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50). Predictive models were accomplished using support vector machine employing 10-fold cross validation technique. The overall predictor showed the Pearson's correlation coefficient of 0.82 on training/testing dataset. Likewise, it also performed equally well on the independent validation dataset. The robustness of the predictive model was confirmed by applicability domain (William's plot) and scatter plot between actual and predicted efficiencies. Further, the data visualization module from chemical clustering analysis displayed the diversity in the NiV inhibitors. Therefore, this web platform would be of immense help to the researchers working in developing effective inhibitors against NiV. The user-friendly web server is freely available on URL: http://bioinfo.imtech.res.in/manojk/antinipah/.
Keywords: Nipah virus; QSAR; database; inhibitors; outbreak; prediction algorithm.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

