Complete Genome Sequence of 3-Chlorobenzoate-Degrading Bacterium Cupriavidus necator NH9 and Reclassification of the Strains of the Genera Cupriavidus and Ralstonia Based on Phylogenetic and Whole-Genome Sequence Analyses
- PMID: 30809202
- PMCID: PMC6379261
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00133
Complete Genome Sequence of 3-Chlorobenzoate-Degrading Bacterium Cupriavidus necator NH9 and Reclassification of the Strains of the Genera Cupriavidus and Ralstonia Based on Phylogenetic and Whole-Genome Sequence Analyses
Abstract
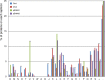
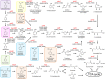
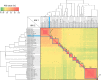
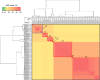
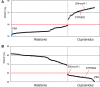
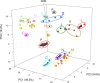
Cupriavidus necator NH9, a 3-chlorobenzoate (3-CB)-degrading bacterium, was isolated from soil in Japan. In this study, the complete genome sequence of NH9 was obtained via PacBio long-read sequencing to better understand the genetic components contributing to the strain's ability to degrade aromatic compounds, including 3-CB. The genome of NH9 comprised two circular chromosomes (4.3 and 3.4 Mb) and two circular plasmids (427 and 77 kb) containing 7,290 coding sequences, 15 rRNA and 68 tRNA genes. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis of the protein-coding sequences in NH9 revealed a capacity to completely degrade benzoate, 2-, 3-, or 4-hydroxybenzoate, 2,3-, 2,5-, or 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate, benzoylformate, and benzonitrile. To validate the identification of NH9, phylogenetic analyses (16S rRNA sequence-based tree and multilocus sequence analysis) and whole-genome sequence analyses (average nucleotide identity, percentage of conserved proteins, and tetra-nucleotide analyses) were performed, confirming that NH9 is a C. necator strain. Over the course of our investigation, we noticed inconsistencies in the classification of several strains that were supposed to belong to the two closely-related genera Cupriavidus and Ralstonia. As a result of whole-genome sequence analysis of 46 Cupriavidus strains and 104 Ralstonia strains, we propose that the taxonomic classification of 41 of the 150 strains should be changed. Our results provide a clear delineation of the two genera based on genome sequences, thus allowing taxonomic identification of strains belonging to these two genera.
Keywords: ANI (average nucleotide identity); Cupriavidus; Ralstonia; TNA (tetra-nucleotide analysis); aromatic degradation; reclassification.
Figures



Comment in
-
Commentary: Complete Genome Sequence of 3-Chlorobenzoate-Degrading Bacterium Cupriavidus necator NH9 and Reclassification of the Strains of the Genera Cupriavidus and Ralstonia Based on Phylogenetic and Whole-Genome Sequence Analyses.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 28;10:2011. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02011. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31555242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

