Component Interaction of ESCRT Complexes Is Essential for Endocytosis-Dependent Growth, Reproduction, DON Production and Full Virulence in Fusarium graminearum
- PMID: 30809208
- PMCID: PMC6379464
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00180
Component Interaction of ESCRT Complexes Is Essential for Endocytosis-Dependent Growth, Reproduction, DON Production and Full Virulence in Fusarium graminearum
Abstract
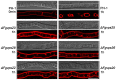
Multivesicular bodies (MVBs) are critical intermediates in the trafficking of ubiquitinated endocytosed surface proteins to the lysosome/vacuole for destruction. Recognizing and packaging ubiquitin modified cargoes to the MVB pathway require ESCRT (Endosomal sorting complexes required for transport) machinery, which consists of four core subcomplexes, ESCRT-0, ESCRT-I, ESCRT-II, and ESCRT-III. Fusarium graminearum is an important plant pathogen that causes head blight of major cereal crops. Our previous results showed that ESCRT-0 is essential for fungal development and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum. We then, in this study, systemically studied the protein-protein interactions within F. graminearum ESCRT-I, -II or -III complex, as well as between ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I, ESCRT-I and ESCRT-II, and ESCRT-II and ESCRT-III complexes and found that loss of any ESCRT component resulted in abnormal function in endocytosis. In addition, ESCRT deletion mutants displayed severe defects in growth, deoxynivalenol (DON) production, virulence, sexual, and asexual reproduction. Importantly genetic complementation with corresponding ESCRT genes fully rescued all these defective phenotypes, indicating the essential role of ESCRT machinery in fungal development and plant infection in F. graminearum. Taken together, the protein-protein interactome and biological functions of the ESCRT machinery is first profoundly characterized in F. graminearum, providing a foundation for further exploration of ESCRT machinery in filamentous fungi.
Keywords: ESCRT complexes; Fusarium graminearum; endocytosis; interactome; pathogenicity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ESCRT-III accessory proteins regulate fungal development and plant infection in Fusarium graminearum.Curr Genet. 2019 Aug;65(4):1041-1055. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00949-z. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30927052
-
Endosomal sorting complexes required for transport-0 is essential for fungal development and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum.Environ Microbiol. 2016 Nov;18(11):3742-3757. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13296. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26971885
-
Genome-Wide Characterization of PX Domain-Containing Proteins Involved in Membrane Trafficking-Dependent Growth and Pathogenicity of Fusarium graminearum.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0232421. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02324-21. Epub 2021 Dec 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34933449 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomics of cereal-Fusarium graminearum interactions: what we have learned so far.Mol Plant Pathol. 2018 Mar;19(3):764-778. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12561. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Mol Plant Pathol. 2018. PMID: 28411402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in genes involved in secondary metabolite synthesis, hyphal development, energy metabolism and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum (teleomorph Gibberella zeae).Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Mar-Apr;32(2):390-402. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.12.007. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 24389085 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and proteomic profiling of urinary exosomes from patients with colorectal cancer.Proteome Sci. 2023 Feb 9;21(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12953-023-00203-y. Proteome Sci. 2023. PMID: 36759883 Free PMC article.
-
FgAP1σ Is Critical for Vegetative Growth, Conidiation, Virulence, and DON Biosynthesis in Fusarium graminearum.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;9(2):145. doi: 10.3390/jof9020145. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836259 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Association of ESCRT-II Proteins with ESCRT-I and ESCRT-III Complexes during Phagocytosis of Entamoeba histolytica.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 9;24(6):5267. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065267. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982336 Free PMC article.
-
FgVps9, a Rab5 GEF, Is Critical for DON Biosynthesis and Pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1714. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01714. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32849361 Free PMC article.
-
The GTPase-Activating Protein FgGyp1 Is Important for Vegetative Growth, Conidiation, and Virulence and Negatively Regulates DON Biosynthesis in Fusarium graminearium.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 21;12:621519. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.621519. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33552040 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

