Sialyllactose and Galactooligosaccharides Promote Epithelial Barrier Functioning and Distinctly Modulate Microbiota Composition and Short Chain Fatty Acid Production In Vitro
- PMID: 30809221
- PMCID: PMC6380229
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00094
Sialyllactose and Galactooligosaccharides Promote Epithelial Barrier Functioning and Distinctly Modulate Microbiota Composition and Short Chain Fatty Acid Production In Vitro
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Sialyllactose and Galactooligosaccharides Promote Epithelial Barrier Functioning and Distinctly Modulate Microbiota Composition and Short Chain Fatty Acid Production In Vitro.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 10;10:762. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00762. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31024573 Free PMC article.
Abstract
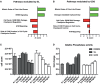
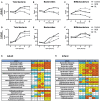
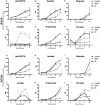
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO) and prebiotic oligosaccharides are proposed to confer several health benefits to the infant. They shape the microbiota, have anti-inflammatory properties, and support epithelial barrier functioning. However, in order to select the best oligosaccharides for inclusion in infant formulas, there is a need to increase our understanding of the specific effects of HMO and prebiotics on the host immune system. Therefore, we investigated the effects of the HMO sialyllactose (SL), and galactooligosaccharides (GOS) on epithelial barrier functioning, microbiota composition, and SCFA production. The effect of GOS and SL on epithelial barrier functioning and microbiota composition was investigated using in vitro models. Epithelial barrier function was investigated by transcriptome analysis of fully polarized Caco-2 cells exposed for 6 h to SL or GOS. In addition, epithelial cell growth, alkaline phosphatase production, and re-epithelization was studied. Further, we investigated the effect of SL and GOS on microbiota composition and SCFA production using in vitro fecal batch cultures. Transcriptome analysis showed that SL and GOS both induced pathways that regulate cell cycle control. This gene-expression profile translated to a phenotype of halted proliferation and included the induction of alkaline phosphatase activity, a marker of epithelial cell differentiation. SL and GOS also promoted re-epithelialization in an in vitro epithelial wound repair assay. SL and GOS did show distinct modulation of microbiota composition, promoting the outgrowth of Bacteroides and bifidobacteria, respectively, which resulted in distinct changes in SCFA production profiles. Our results show that SL and GOS can both modulate epithelial barrier function by inducing differentiation and epithelial wound repair, but differentially promote the growth of specific genera in the microbiota, which is associated with differential changes in SCFA profiles.
Keywords: epithelium; galactooligosaccharides; microbiota; short chain fatty acids; sialyllactose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct fermentation of human milk oligosaccharides 3-FL and LNT2 and GOS/inulin by infant gut microbiota and impact on adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 to gut epithelial cells.Food Funct. 2021 Dec 13;12(24):12513-12525. doi: 10.1039/d1fo02563e. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 34811557
-
Utilization of major fucosylated and sialylated human milk oligosaccharides by isolated human gut microbes.Glycobiology. 2013 Nov;23(11):1281-92. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwt065. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Glycobiology. 2013. PMID: 24013960 Free PMC article.
-
The oligosaccharides 6'-sialyllactose, 2'-fucosyllactose or galactooligosaccharides do not directly modulate human dendritic cell differentiation or maturation.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 10;13(7):e0200356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200356. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29990329 Free PMC article.
-
Varied Pathways of Infant Gut-Associated Bifidobacterium to Assimilate Human Milk Oligosaccharides: Prevalence of the Gene Set and Its Correlation with Bifidobacteria-Rich Microbiota Formation.Nutrients. 2019 Dec 26;12(1):71. doi: 10.3390/nu12010071. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31888048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress on health effects and biosynthesis of two key sialylated human milk oligosaccharides, 3'-sialyllactose and 6'-sialyllactose.Biotechnol Adv. 2023 Jan-Feb;62:108058. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108058. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Biotechnol Adv. 2023. PMID: 36372185 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Milk Oligosaccharides Impact Cellular and Inflammatory Gene Expression and Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 29;13:907529. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907529. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844612 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterial β-Galactosidase-Mediated Production of Galacto-Oligosaccharides: Structural and Preliminary Functional Assessments.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 28;12:750635. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.750635. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34777303 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of the Effects of Commercial Prebiotic GOS and FOS Products on Human Colonic Caco-2 Cells.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 30;12(5):1281. doi: 10.3390/nu12051281. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32366023 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrogenic effect of galactosyl and mannosyl carbohydrates and their regulation on piglet intestinal microbiota.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Mar;107(5-6):1903-1916. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12436-0. Epub 2023 Feb 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36795139
-
A bridge for short-chain fatty acids to affect inflammatory bowel disease, type 1 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease positively: by changing gut barrier.Eur J Nutr. 2021 Aug;60(5):2317-2330. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02431-w. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Eur J Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33180143 Review.
References
-
- van Herwijnen MJC, Zonneveld MI, Goerdayal S, Nolte – 't Hoen ENM, Garssen J, Stahl B, et al. . Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human milk-derived extracellular vesicles unveils a novel functional proteome distinct from other milk components. Mol Cell Proteomics (2016) 15:3412–23. 10.1074/mcp.M116.060426 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

