Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Caused by Warfarin after Rifampicin Discontinuation
- PMID: 30809261
- PMCID: PMC6364120
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4917856
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Caused by Warfarin after Rifampicin Discontinuation
Abstract
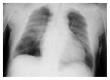
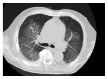
An 83-year-old man under warfarin therapy presented for assessment of prolonged prothrombin time and cough. High-resolution computed tomography findings of the chest showed diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. His international normalized ratio (INR) was 11.89. He had been treated with rifampicin for a persistent infection, but this had been discontinued about two months before admission. Rifampicin suppresses the anticoagulant activity of warfarin, which can lead to a need for increased doses of warfarin to achieve and maintain a therapeutic INR. More frequent INR monitoring is needed even after discontinuing rifampicin.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

