Cell Therapy for Retinal Dystrophies: From Cell Suspension Formulation to Complex Retinal Tissue Bioengineering
- PMID: 30809263
- PMCID: PMC6364130
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4568979
Cell Therapy for Retinal Dystrophies: From Cell Suspension Formulation to Complex Retinal Tissue Bioengineering
Abstract
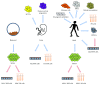
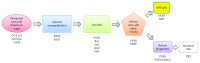
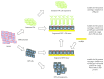
Retinal degeneration is an irreversible phenomenon caused by various disease conditions including age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinitis pigmentosa (RP). During the course of these diseases, photoreceptors (PRs) are susceptible to degeneration due to their malfunctions or to a primary dysfunction of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Once lost, these cells could not be endogenously regenerated in humans, and cell therapy to replace the lost cells is one of the promising strategies to recover vision. Depending on the nature of the primary defect and the stage of the disease, RPE cells, PRs, or both might be transplanted to achieve therapeutic effects. We describe in this review the current knowledge and recent progress to develop such approaches. The different cell sources proposed for cell therapy including human pluripotent stem cells are presented with their advantages and limits. Another critical aspect described herein is the pharmaceutical formulation of the end product to be delivered into the eye of patients. Finally, we also outline the future research directions in order to develop a complex multilayered retinal tissue for end-stage patients.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

