Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy and non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in Asian T2DM patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 30809489
- PMCID: PMC6376231
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2019.02.19
Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy and non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in Asian T2DM patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the pooled prevalence of diabetic retinopathy (DR), proliferative DR (PDR) and nonproliferative DR (NPDR) in Asian type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods: We performed a systematic search online search using PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, the Cochrane Library, and China WeiPu Library to identify eligible studies that reported the prevalence of DR, PDR and NPDR in Asian T2DM patients. Effect size (ES) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to evaluate the prevalence of DR, PDR and NPDR in Asian T2DM patients, respectively.
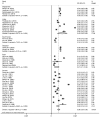
Results: There were 41 references and 48 995 T2DM patients involved in this study. The prevalence of DR, PDR, and NPDR was 28%, 6%, and 27% in T2DM patients, respectively; while the prevalence of PDR and NPDR in DR patients was 17% and 83%, respectively. Subgroup analysis showed that prevalence of DR in T2DM patients from Singaporean, Indian, South Korean, Malaysian, Asian, and Chinese was 33%, 42%, 16%, 35%, 21% and 25%, respectively. In T2DM patients with NPDR from Indian, South Korean, Malaysian, Asian, Chinese, higher prevalence was found than that in PDR patients (45% vs 17%, 13% vs 3%, 30% vs 5%, 23% vs 2% and 22% vs 3%), as well as in DR patients (74% vs 26%, 81% vs 19%, 86% vs 14%, 92% vs 8% and 85% vs 15%). The prevalence of PDR in T2DM from India was higher than patients from other locations of Asia, and the same results were also observed in NPDR patients.
Conclusion: In either T2DM Asian patients or DR patients, NPDR is more common than PDR. Based on our results, we should pay more attention to NPDR screening and management in T2DM patients, and we also recommend suitable interventions to prevent its progression.
Keywords: Asian; nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy; prevalence; proliferative diabetic retinopathy; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Hod M, Kapur A, Sacks DA, Hadar E, Agarwal M, di Renzo GC, Roura LC, McIntyre HD, Morris JL, Divakar H. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) Initiative on gestational diabetes mellitus: a pragmatic guide for diagnosis, management, and care. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2015;131:S173–S211. - PubMed
-
- Vinik AI, Nevoret ML, Casellini C, Parson H. Diabetic neuropathy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2013;42(4):747–787. - PubMed
-
- Yamagishi S, Imaizumi T. Diabetic vascular complications: pathophysiology, biochemical basis and potential therapeutic strategy. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(18):2279–2299. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources