Promising Plant-Derived Adjuvants in the Development of Coccidial Vaccines
- PMID: 30809529
- PMCID: PMC6379251
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00020
Promising Plant-Derived Adjuvants in the Development of Coccidial Vaccines
Abstract
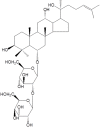
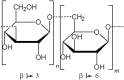
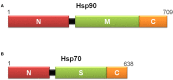
Coccidial parasites cause medical and veterinary diseases worldwide, frequently leading to severe illness and important economic losses. At present, drugs, chemotherapeutics and prophylactic vaccines are still missing for most of the coccidial infections. Moreover, the development and administration of drugs and chemotherapeutics against these diseases would not be adequate in livestock, since they may generate unacceptable residues in milk and meat that would avoid their commercialization. In this scenario, prophylactic vaccines emerge as the most suitable approach. Subunit vaccines have proven to be biologically safe and economically viable, allowing researchers to choose among the best antigens against each pathogen. However, they are generally poorly immunogenic and require the addition of adjuvant compounds to the vaccine formulation. During the last decades, research involving plant immunomodulatory compounds has become an important field of study based on their potential pharmaceutical applications. Some plant molecules such as saponins, polysaccharides, lectins and heat shock proteins are being explored as candidates for adjuvant/carriers formulations. Moreover, plant-derived immune stimulatory compounds open the possibility to attain the main goal in adjuvant research: a safe and non-toxic adjuvant capable of strongly boosting and directing immune responses that could be incorporated into different vaccine formulations, including mucosal vaccines. Here, we review the immunomodulatory properties of several plant molecules and discuss their application and future perspective as adjuvants in the development of vaccines against coccidial infections.
Keywords: coccidial parasites; heat shock proteins; lectins; plant-derived adjuvants; polysaccharides; saponins; vaccines.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization Report of the Second WHO Stakeholders Meeting on Gambiense Human African Trypanosomiasis Elimination. Geneva: (2016). p 21–3.
-
- World Health Organization Global leishmaniasis update, 2006–2015: a turning point in leishmaniasis surveillance. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. (2017) 92:557–72. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . World Malaria Report 2017. Geneva. World Health Organization; (2017).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

