Interplay of non-coding RNAs and approved antimetabolites such as gemcitabine and pemetrexed in mesothelioma
- PMID: 30809600
- PMCID: PMC6257890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2018.11.001
Interplay of non-coding RNAs and approved antimetabolites such as gemcitabine and pemetrexed in mesothelioma
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.Noncoding RNA Res. 2020 Nov 7;5(4):219. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.11.001. eCollection 2020 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020. PMID: 33294747 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Gemcitabine and pemetrexed are clinically approved antimetabolites for the therapy of mesothelioma diseases. These drugs are often applied in combination with platinum complexes and other drugs. The activity of antimetabolites depended on the expression levels of certain non-coding RNAs, in particular, of small microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). The development of tumor resistance towards antimetabolites was regulated by non-coding RNAs. An overview of the interplay between gemcitabine/pemetrexed antimetabolites and non-coding RNAs in mesothelioma is provided. Further to this, various non-coding RNA-modulating agents are discussed which displayed positive effects on gemcitabine or pemetrexed treatment of mesothelioma diseases. A detailed knowledge of the connections of non-coding RNAs with antimetabolites will be constructive for the design of improved therapies in future.
Keywords: AKBA, 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid; Anticancer drugs; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; DADS, diallyl sulfide; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; DIM, 3,3‘-diindolylmethane; DMPM, diffuse malignant peritoneal mesothelioma; EGCG, epigallocatechin-3-gallate; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Gemcitabine; HOTAIR, HOX transcript antisense RNA; I3C, indole-3-carbinol; Long non-coding RNA; MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; MPM, malignant pleural mesothelioma; Mesothelioma; MicroRNA; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; NaB, sodium butyrate; PDCD4, programmed cell death 4; PEG, polyethylene glycole; PEITC, phenethylisothiocyanate; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Pemetrexed; RA, retinoic acid; SAHA, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; SFN, sulforaphane; TSA, trichostatin A.
Figures
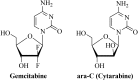
Similar articles
-
Relations between approved platinum drugs and non-coding RNAs in mesothelioma.Noncoding RNA Res. 2018 Aug 30;3(4):161-173. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2018.08.001. eCollection 2018 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2018. PMID: 30809599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA/microRNA-modulatory dietary factors and natural products for improved cancer therapy and prevention: Alkaloids, organosulfur compounds, aliphatic carboxylic acids and water-soluble vitamins.Noncoding RNA Res. 2016 Sep 3;1(1):51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2016.09.001. eCollection 2016 Oct. Noncoding RNA Res. 2016. PMID: 30159411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Irinotecan and Gemcitabine as Second-Line Treatment in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma following Platinum plus Pemetrexed Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Study.Oncology. 2021;99(3):161-168. doi: 10.1159/000510691. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Oncology. 2021. PMID: 33053560
-
Phase II trial of pemetrexed and gemcitabine in chemotherapy-naive malignant pleural mesothelioma.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Mar 20;26(9):1465-71. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.7611. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18349397 Clinical Trial.
-
In Silico and In Vitro Analyses of LncRNAs as Potential Regulators in the Transition from the Epithelioid to Sarcomatoid Histotype of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM).Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 26;19(5):1297. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051297. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29701689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
lncRNA ZEB2-AS1 Aggravates Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma via Suppressing PTEN Level.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 7;25:8363-8370. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918922. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31695021 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Odgerel C.-O., Takahashi K., Sorahan T., Driscoll T., Fitzmaurice C., Yoko-o M., Sawanyawisuth K., Furuya S., Tanaka F., Horie S., van Zandwijk N., Takala J. Estimation of the global burden of mesothelioma deaths from incomplete national mortality data. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017;74:851–858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Romano M., Catalano A., Nutini M., D'Urbano E., Crescenzi C., Claria J., Libner R., Davi G., Procopio A. 5-Lipoxygenase regulates malignant mesothelial cell survival: involvement of vascular endothelial growth factor. FASEB J. 2001;15:2326–2336. - PubMed
-
- Truini A., Coco S., Genova C., Mora M., Dal Bello M.G., Vanni I., Alama A., Rijavec E., Barletta G., Biello F., Maggioni C., Grossi F. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of microRNA in malignant pleural mesothelioma. MicroRNA. 2016;5:12–18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

