Plasma ctDNA monitoring during epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (JP-CLEAR trial)
- PMID: 30809659
- PMCID: PMC6541116
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hyz023
Plasma ctDNA monitoring during epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (JP-CLEAR trial)
Abstract
Background: Osimertinib, a third generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), is active against EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) resistant to first-/second-generation EGFR-TKIs with the T790M mutation. T790M monitoring in plasma circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in patients receiving EGFR-TKIs is less invasive than re-biopsy and could provide valuable clinical information.
Methods: Patients with advanced or postoperative recurrent NSCLC with sensitizing EGFR mutations who were planned to receive or were receiving first-/second-generation EGFR-TKI treatment without disease progression were eligible for enrollment. Plasma samples at baseline and every 1-2 months thereafter were analyzed for EGFR mutation status using the cobas®EGFR Mutation Test v2.
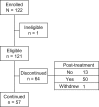
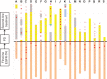
Results: Between September 2016 and March 2017, 122 patients at 15 Japanese institutions were enrolled. In August 2018, 1291 plasma samples from 121 patients were analyzed for EGFR mutation status. At baseline, a sensitizing EGFR mutation was detected in 29 (23.9%) of 121 patients and T790M mutation was detected in three (2.5%). At follow-up, 66 (54.5%) patients experienced disease progression and 64 (52.9%) discontinued first-line EGFR-TKI treatment. Twenty-two (18.2%) patients showed T790M in plasma ctDNA, of which 15(68.2%) received osimertinib. Although 31 patients received re-biopsy to examine EGFR status at disease progression, T790M was detected in only nine (22.0%) patients, of which 7 (77.8%) received osimertinib.
Conclusions: ctDNA monitoring during EGFR-TKI treatment is useful for detecting T790M mutation. The efficacy of osimertinib treatment based on T790M status in plasma ctDNA remains to be established, warranting further research.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; T790M; ctDNA; liquid biopsy; osimertinib.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib in the Second-Line Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with the EGFR T790M Mutation, Detected from Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 2.Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Apr;51(2):777-787. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.387. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30189719 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma screening for the T790M mutation of EGFR and phase 2 study of osimertinib efficacy in plasma T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer: West Japan Oncology Group 8815L/LPS study.Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;126(9):1940-1948. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32749. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32022929 Clinical Trial.
-
Circulating Tumor DNA T790M Testing as a Predictor of Osimertinib Efficacy in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single Center Experience.Isr Med Assoc J. 2019 Jun;21(6):394-398. Isr Med Assoc J. 2019. PMID: 31280508
-
Osimertinib for EGFR T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;10(1):31-38. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2017.1265446. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27885838 Review.
-
Osimertinib: A third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer with the acquired Thr790Met mutation.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018 Jul;24(5):379-388. doi: 10.1177/1078155217712401. Epub 2017 May 31. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018. PMID: 28565936 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Liquid Biopsy Based on ctDNA/cfDNA Replace Tissue Biopsy for the Precision Treatment of EGFR-Mutated NSCLC?J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 10;12(4):1438. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041438. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36835972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-Free Tumor DNA (ctDNA) Utility in Detection of Original Sensitizing and Resistant EGFR Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Curr Oncol. 2022 Feb 14;29(2):1107-1116. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29020094. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35200593 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-dependent mechanisms of resistance to osimertinib determined by ctDNA NGS analysis identify patients with better outcome.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Nov;10(11):4084-4094. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-679. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35004240 Free PMC article.
-
The Validity and Predictive Value of Blood-Based Biomarkers in Prediction of Response in the Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 30;12(5):1120. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051120. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32365836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of different methods for detecting T790M mutation in the plasma of patients with advanced NSCLC after developing resistance to first-generation EGFR-TKIs in a real-world clinical setting.Mol Clin Oncol. 2022 Apr;16(4):88. doi: 10.3892/mco.2022.2521. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Mol Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35251639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. . Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:121–8. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. . Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010;362:2380–8. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. . Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicenter, open-label, randomized phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239–46. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. . Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicenter, open-label, randomized, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2011;12:735–42. - PubMed
-
- Wu YL, Zhou C, Hu CP, et al. . Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014;15:213–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

