Antibody-targeted chromatin enables effective intracellular delivery and functionality of CRISPR/Cas9 expression plasmids
- PMID: 30809660
- PMCID: PMC6547418
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz137
Antibody-targeted chromatin enables effective intracellular delivery and functionality of CRISPR/Cas9 expression plasmids
Abstract
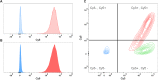
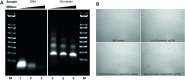
We report a novel system for efficient and specific targeted delivery of large nucleic acids to and into cells. Plasmid DNA and core histones were assembled to chromatin by salt gradient dialysis and subsequently connected to bispecific antibody derivatives (bsAbs) via a nucleic acid binding peptide bridge. The resulting reconstituted vehicles termed 'plasmid-chromatin' deliver packaged nucleic acids to and into cells expressing antigens that are recognized by the bsAb, enabling intracellular functionality without detectable cytotoxicity. High efficiency of intracellular nucleic acid delivery is revealed by intracellular expression of plasmid encoded genes in most (∼90%) target cells to which the vehicles were applied under normal growth/medium conditions in nanomolar concentrations. Specific targeting, uptake and transgene expression depends on antibody-mediated cell surface binding: plasmid chromatin of identical composition but with non-targeting bsAbs or without bsAbs is ineffective. Examples that demonstrate applicability, specificity and efficacy of antibody-targeted plasmid chromatin include reporter gene constructs as well as plasmids that enable CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing of target cells.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of an in vivo cleavable donor plasmid for targeted transgene integration by CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cas12a.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 22;12(1):17775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22639-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36272994 Free PMC article.
-
Genome editing with the donor plasmid equipped with synthetic crRNA-target sequence.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 24;10(1):14120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70804-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32839482 Free PMC article.
-
Robust genome editing in adult vascular endothelium by nanoparticle delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 plasmid DNA.Cell Rep. 2022 Jan 4;38(1):110196. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110196. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 34986352 Free PMC article.
-
An Era of CRISPR/ Cas9 Mediated Plant Genome Editing.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2018;26:47-54. doi: 10.21775/cimb.026.047. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 28879855 Review.
-
Characterization and Repurposing of Type I and Type II CRISPR-Cas Systems in Bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2019 Jan 4;431(1):21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.09.013. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30261168 Review.
Cited by
-
Liposomal delivery of CRISPR/Cas9.Cancer Gene Ther. 2020 Aug;27(7-8):515-527. doi: 10.1038/s41417-019-0141-7. Epub 2019 Nov 2. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020. PMID: 31676843 Review.
-
High-throughput development and characterization of new functional nanobodies for gene regulation and epigenetic control in human cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 3:2024.11.01.621523. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.01.621523. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39554150 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Targeting cancer epigenetics with CRISPR-dCAS9: Principles and prospects.Methods. 2021 Mar;187:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Methods. 2021. PMID: 32315755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

