Comparison of Six Automated Immunoassays With Isotope-Diluted Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Total Thyroxine Measurement
- PMID: 30809984
- PMCID: PMC6400722
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.4.381
Comparison of Six Automated Immunoassays With Isotope-Diluted Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Total Thyroxine Measurement
Abstract
Background: Accurate serum total thyroxine (TT4) measurement is important for thyroid disorder diagnosis and management. We compared the performance of six automated immunoassays with that of isotope-diluted liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (ID-LC-MS/MS) as the reference method. We also evaluated the correlation of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) with TT4 measured by ID-LC-MS/MS and immunoassays.
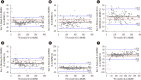
Methods: Serum was collected from 156 patients between October 2015 and January 2016. TT4 was measured by immunoassays from Abbott (Architect), Siemens (ADVIA Centaur XP), Roche (E601), Beckman-Coulter (Dxi800), Autobio (Autolumo A2000), and Mindray (CL-1000i), and by ID-LC-MS/MS. Results were analyzed using Passing-Bablok regression and Bland-Altman plots. Minimum requirements based on biological variation were as follows: a mean bias of ≤4.5% and total imprecision (CV) of ≤3.7%.
Results: All immunoassays showed a correlation >0.945 with ID-LC-MS/MS; however, the slope of the Passing-Bablok regression line varied from 0.886 (Mindray) to 1.23 (Siemens) and the intercept from -12.8 (Siemens) to 4.61 (Mindray). Only Autobio, Beckman-Coulter, and Roche included the value of one in the 95% confidence interval for slope. The mean bias ranged from -10.8% (Abbott) to 9.0% (Siemens), with the lowest value noted for Roche (3.5%) and the highest for Abbott (-10.8%). Only Abbott and Roche showed within-run and total CV ≤3.7%.
Conclusions: Though all immunoassays correlated strongly with ID-LC-MS/MS, most did not meet the minimum clinical requirement. Laboratories and immunoassay manufacturers must be aware of these limitations.
Keywords: Evaluation; Immunoassay; Isotope-diluted liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry; Performance; Thyroxine.
© The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures

References
-
- Goemann IM, Romitti M, Meyer ELS, Wajner SM, Maia AL. Role of thyroid hormones in the neoplastic process: an overview. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017;24:R367–R385. - PubMed
-
- Baloch Z, Carayon P, Conte-Devolx B, Demers LM, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Henry JF, et al. Laboratory medicine practice guidelines. Laboratory support for the diagnosis and monitoring of thyroid disease. Thyroid. 2003;13:3–126. - PubMed
-
- Mendel CM. The free hormone hypothesis: a physiologically based mathematical model. Endocr Rev. 1989;10:232–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

