A dual blocker of endothelin A/B receptors mitigates hypertension but not renal dysfunction in a rat model of chronic kidney disease and sleep apnea
- PMID: 30810064
- PMCID: PMC7132313
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00018.2019
A dual blocker of endothelin A/B receptors mitigates hypertension but not renal dysfunction in a rat model of chronic kidney disease and sleep apnea
Abstract
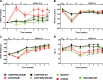
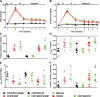
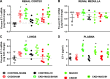
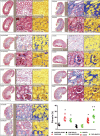
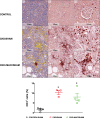
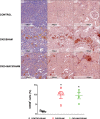
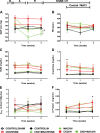
Obstructive sleep apnea is characterized by recurrent episodes of pharyngeal collapse during sleep, resulting in intermittent hypoxia (IH), and is associated with a high incidence of hypertension and accelerated renal failure. In rodents, endothelin (ET)-1 contributes to IH-induced hypertension, and ET-1 levels inversely correlate with glomerular filtration rate in patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease (CKD). Therefore, we hypothesized that a dual ET receptor antagonist, macitentan (Actelion Pharmaceuticals), will attenuate and reverse hypertension and renal dysfunction in a rat model of combined IH and CKD. Male Sprague-Dawley rats received one of three diets (control, 0.2% adenine, and 0.2% adenine + 30 mg·kg-1·day-1 macitentan) for 2 wk followed by 2 wk of recovery diet. Rats were then exposed for 4 wk to air or IH (20 short exposures/h to 5% O2-5% CO2 7 h/day during sleep). Macitentan prevented the increases in mean arterial blood pressure caused by CKD, IH, and the combination of CKD + IH. However, macitentan did not improve kidney function, fibrosis, and inflammation. After CKD was established, rats were exposed to air or IH for 2 wk, and macitentan feeding continued for 2 more wk. Macitentan reversed the hypertension in IH, CKD, and CKD + IH groups without improving renal function. Our data suggest that macitentan could be an effective antihypertensive in patients with CKD and irreversible kidney damage as a way to protect the heart, brain, and eyes from elevated arterial pressure, but it does not reverse toxin-induced tubule atrophy.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; endothelin; intermittent hypoxia; macitentan; obstructive sleep apnea.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intermittent hypoxia exacerbates increased blood pressure in rats with chronic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):F927-F941. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00420.2017. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29897288 Free PMC article.
-
Selective ETA vs. dual ETA/B receptor blockade for the prevention of sunitinib-induced hypertension and albuminuria in WKY rats.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Aug 1;116(10):1779-1790. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz260. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 31593221
-
Novel dual endothelin receptor antagonist macitentan reverses severe pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014 Nov;64(5):473-80. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000141. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25084082
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of macitentan , a novel endothelin receptor antagonist for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015 Mar;11(3):437-49. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2015.1000859. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25604973 Review.
-
Safety, efficacy, and clinical utility of macitentan in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 May 18;10:1675-82. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S88612. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 27274200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology Collections: Hypertension.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):F1001-F1002. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00572.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33166184 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Chronic Kidney Disease Induced by Hypertension and Diabetes.Cells. 2025 May 16;14(10):729. doi: 10.3390/cells14100729. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelin receptors in renal interstitial cells do not contribute to the development of fibrosis during experimental kidney disease.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Oct;473(10):1667-1683. doi: 10.1007/s00424-021-02604-4. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 34355294 Free PMC article.
-
Future of Uremic Toxin Management.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 28;16(11):463. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110463. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporin-2 in the early stages of the adenine-induced chronic kidney disease model.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 30;20(1):e0314827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314827. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39883648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali BH, Al Za’abi M, Ramkumar A, Yasin J, Nemmar A. Anemia in adenine-induced chronic renal failure and the influence of treatment with gum acacia thereon. Physiol Res 63: 351–358, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

