Retinoic acid increases the effect of bone morphogenetic protein type 2 on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells
- PMID: 30810639
- PMCID: PMC6382324
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-7757-2018-0317
Retinoic acid increases the effect of bone morphogenetic protein type 2 on osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells
Abstract
Background: Bone morphogenetic protein type 2 (BMP-2) and retinoic acid (RA) are osteoinductive factors that stimulate endogenous mechanisms of bone repair which can be applied on management of osseous defects in oral and maxillofacial fields.
Objective: Considering the different results of RA on osteogenesis and its possible use to substitute/potency BMP-2 effects, this study evaluated the outcomes of BMP-2, RA, and BMP-2+RA treatments on in vitro osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) and the signaling pathway(s) involved.
Material and methods: ASCs were treated every other day with basic osteogenic medium (OM) alone or supplemented with BMP-2, RA, or BMP-2+RA. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was determined using the r-nitrophenol method. Extracellular matrix mineralization was evaluated using von Kossa staining and calcium quantification. Expression of osteonectin and osteocalcin mRNA were determined using qPCR. Smad1, Smad4, phosphorylated Smad1/5/8, BMP-4, and BMP-7 proteins expressions were analyzed using western blotting. Signaling pathway was evaluated using the IPA® software.
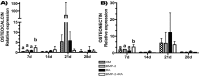
Results: RA promoted the highest ALP activity at days 7, 14, 21, and 28, in comparison to BMP-2 and BMP-2+RA. BMP-2+RA best stimulated phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 protein expression at day 7 and Smad4 expression at days 7, 14, 21, and 28. Osteocalcin and osteonectin mRNA expressions were best stimulated by BMP-2+RA at day 7. Matrix mineralization was most improved by BMP-2+RA at days 12 and 32. Additionally, BMP-2+RA promoted the highest BMP signaling pathway activation at days 7 and 14, and demonstrated more activation of differentiation of bone-forming cells than OM alone.
Conclusions: In summary, RA increased the effect of BMP-2 on osteogenic differentiation of human ASCs.
Figures


References
-
- Urist MR. Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965;150(3698):893–899. - PubMed
-
- Alonso N, Tanikawa DY, Freitas RS, Canan L, Jr, Ozawa TO, Rocha DL. Evaluation of maxillary alveolar reconstruction using a resorbable collagen sponge with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in cleft lip and palate patients. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(5):1183–1189. - PubMed
-
- Shah MM, Smyth MD, Woo AS. Adverse facial edema associated with off-label use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in cranial reconstruction for craniosynostosis. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008;1(3):255–257. - PubMed
-
- Boyne PJ, Marx RE, Nevins M, Triplett G, Lazaro E, Lilly LC, et al. A feasibility study evaluating rhBMP-2/absorbable collagen sponge for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1997;17(1):11–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

