Validity of the Apple Watch® for monitoring push counts in people using manual wheelchairs
- PMID: 30811310
- PMCID: PMC7952070
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2019.1576444
Validity of the Apple Watch® for monitoring push counts in people using manual wheelchairs
Abstract
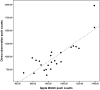
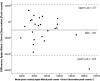
Objective: A recent Apple Watch® activity-monitoring innovation permits manual wheelchair users to monitor daily push counts. This study evaluated the validity of the Apple Watch® push count estimate.Design: Criterion validity.Setting: Southern Finland and Southeast Queensland, Australia.Participants: Twenty-six manual wheelchair users from Finland and Australia were filmed completing a standardized battery of activities while wearing the Apple Watch® (dominant wrist).Outcome Measures: Wheelchair pushes as determined by the Apple Watch® were compared to directly observed pushes.Results: Agreement between Apple Watch® push counts and directly observed pushes was evaluated using Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC), Pearson correlations and Bland-Altman analyses. Apple Watch® pushes and directly observed push counts were strongly correlated (ICC = 0.77, P < 0.01) (r = 0.84, P < 0.01). Bland Altman plots indicated that the Apple Watch® underestimated push counts (M = -103; 95% ULoA = 217; LLoA = -423 pushes). Mean absolute percentage error was 13.5% which is comparable to studies evaluating agreement between pedometer-based step counts and directly observed steps.Conclusion: Apple Watch® push-count estimates are acceptable for personal, self-monitoring purposes and for research entailing group-level analyses, but less acceptable where accurate push-count measures for an individual is required.
Keywords: Apple Watch®; Monitoring; Physical activity; Push counts; Wheelchair.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Bureau of Statistics . Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia: Summary of Findings, 2015 2016 [Cat no. 4430.0]. Available from http://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/Latestproducts/4430.0Main%20Feat....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
