CoPhosK: A method for comprehensive kinase substrate annotation using co-phosphorylation analysis
- PMID: 30811403
- PMCID: PMC6411229
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006678
CoPhosK: A method for comprehensive kinase substrate annotation using co-phosphorylation analysis
Abstract
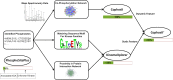
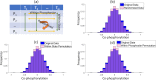
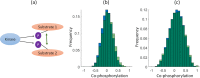
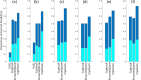
We present CoPhosK to predict kinase-substrate associations for phosphopeptide substrates detected by mass spectrometry (MS). The tool utilizes a Naïve Bayes framework with priors of known kinase-substrate associations (KSAs) to generate its predictions. Through the mining of MS data for the collective dynamic signatures of the kinases' substrates revealed by correlation analysis of phosphopeptide intensity data, the tool infers KSAs in the data for the considerable body of substrates lacking such annotations. We benchmarked the tool against existing approaches for predicting KSAs that rely on static information (e.g. sequences, structures and interactions) using publically available MS data, including breast, colon, and ovarian cancer models. The benchmarking reveals that co-phosphorylation analysis can significantly improve prediction performance when static information is available (about 35% of sites) while providing reliable predictions for the remainder, thus tripling the KSAs available from the experimental MS data providing to a comprehensive and reliable characterization of the landscape of kinase-substrate interactions well beyond current limitations.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: The patent application is pending from Case Western Reserve University. The patent is about the methodology to identify enzyme-substrate association using co-substrate analysis.
Figures



References
-
- Wisniewski J.R., et al. (2010) "Brain phosphoproteome obtained by a FASP-based method reveals plasma membrane protein topology", Journal of proteome research 9.6, 3280–3289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

