NADPH Oxidase Mediates Membrane Androgen Receptor-Induced Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 30811529
- PMCID: PMC6435014
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2018-01079
NADPH Oxidase Mediates Membrane Androgen Receptor-Induced Neurodegeneration
Abstract
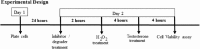
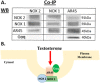
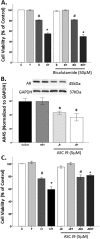
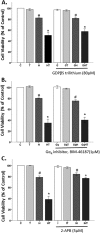
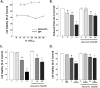
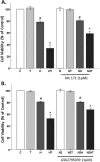
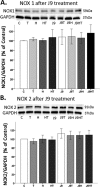
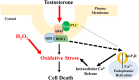
Oxidative stress (OS) is a common characteristic of several neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson disease (PD). PD is more prevalent in men than in women, indicating the possible involvement of androgens. Androgens can have either neuroprotective or neurodamaging effects, depending on the presence of OS. Specifically, in an OS environment, androgens via a membrane-associated androgen receptor (mAR) exacerbate OS-induced damage. To investigate the role of androgens on OS signaling and neurodegeneration, the effects of testosterone and androgen receptor activation on the major OS signaling cascades, the reduced form of NAD phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX)1 and NOX2 and the Gαq/inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R), were examined. To create an OS environment, an immortalized neuronal cell line was exposed to H2O2 prior to cell-permeable/cell-impermeable androgens. Different inhibitors were used to examine the role of G proteins, mAR, InsP3R, and NOX1/2 on OS generation and cell viability. Both testosterone and DHT/3-O-carboxymethyloxime (DHT)-BSA increased H2O2-induced OS and cell death, indicating the involvement of an mAR. Furthermore, classical AR antagonists did not block testosterone's negative effects in an OS environment. Because there are no known antagonists specific for mARs, an AR protein degrader, ASC-J9, was used to block mAR action. ASC-J9 blocked testosterone's negative effects. To determine OS-related signaling mediated by mAR, this study examined NOX1, NOX2, Gαq. NOX1, NOX2, and the Gαq complex with mAR. Only NOX inhibition blocked testosterone-induced cell loss and OS. No effects of blocking either Gαq or G protein activation were observed on testosterone's negative effects. These results indicate that androgen-induced OS is via the mAR-NOX complex and not the mAR-Gαq complex.
Copyright © 2019 Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Sherer TB, Chowdhury S, Peabody K, Brooks DW. Overcoming obstacles in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2012;27(13):1606–1611. - PubMed
-
- Dorsey ER, Constantinescu R, Thompson JP, Biglan KM, Holloway RG, Kieburtz K, Marshall FJ, Ravina BM, Schifitto G, Siderowf A, Tanner CM. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology. 2007;68(5):384–386. - PubMed
-
- Ross GW, Petrovitch H, Abbott RD, Nelson J, Markesbery W, Davis D, Hardman J, Launer L, Masaki K, Tanner CM, White LR. Parkinsonian signs and substantia nigra neuron density in decendents elders without PD. Ann Neurol. 2004;56(4):532–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

