Bidirectional regulation between 1st trimester HTR8/SVneo trophoblast cells and in vitro differentiated Th17/Treg cells suggest a fetal-maternal regulatory loop in human pregnancy
- PMID: 30811743
- PMCID: PMC6594139
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.13106
Bidirectional regulation between 1st trimester HTR8/SVneo trophoblast cells and in vitro differentiated Th17/Treg cells suggest a fetal-maternal regulatory loop in human pregnancy
Abstract
Problem: During normal pregnancy, delicate crosstalk is established between fetus-derived trophoblasts and maternal immune cells to ensure maternal-fetal tolerance and successful placentation. Dysfunction in these interactions has been highly linked to certain pregnancy complications.
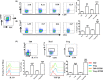
Method of study: Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultivated with or without 1st trimester derived trophoblast cell line HTR8/SVneo cells in the absence or presence of T helper 17 (Th17) or regulatory (Treg)cell-inducing differentiation conditions. After 5 days of co-culture, HTR8/SVneo cells and CD4+ T cells were harvested and analyzed using flow cytometry.
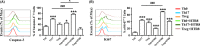
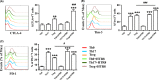
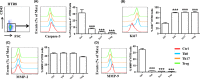
Results: CD4+ T cells exposed to HTR8/SVneo cells showed enhanced induction of CD4+ Foxp3+ Treg cells with strong expression of TGF-β1 and inhibitory molecules (cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein-4 [CTLA-4], T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 [Tim-3], and programmed cell death-1 [PD-1]). Though not effecting Th17 differentiation, exposure to HTR8/SVneo cells promoted increased expression of proliferative and apoptotic markers on Th17 cells. Co-culture with Th0 cells, or differentiated Th17 or Treg cells, down-regulated Caspase-3 and MMP-9 (but not MMP-2) expression in HTR8/SVneo cells, while promoting Ki67 expression.
Conclusions: HTR8/SVneo cells regulated maternal CD4+ T-cell differentiation, resulting in the expansion of immunosuppressive Treg cells, while CD4+ T cells might promote the growth, and control the invasiveness of HTR8/SVneo cells. Thus, a bidirectional regulatory loop might exist between trophoblasts and maternal immune cell subsets, thereby promoting harmonious maternal-fetal crosstalk.
Keywords: HTR8/SVneo cells; Th17 cells; Treg cells; pregnancy; trophoblasts.
© 2019 The Authors American Journal of Reproductive Immunology Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Arck PC, Hecher K. Fetomaternal immune cross‐talk and its consequences for maternal and offspring's health. Nat Med. 2013;19(5):548‐556. - PubMed
-
- Al‐Khan A, Bulmer JN, Chantraine F, et al. IFPA Meeting 2012 Workshop Report III: trophoblast deportation, gestational trophoblastic disease, placental insufficiency and fetal growth restriction, trophoblast over‐invasion and accreta‐related pathologies, placental thrombosis and fibrinolysis. Placenta. 2013;34(Suppl):S11‐S16. - PubMed
-
- Chaouat G, Ledee‐Bataille N, Dubanchet S, et al. Reproductive immunology 2003: reassessing the Th1/Th2 paradigm? Immunol Lett. 2004;92(3):207‐214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31570920/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 31700799/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81630036/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 91542116/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2015CB943300/National Basic Research Program of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

