Early characteristics of fulminant myocarditis vs non-fulminant myocarditis: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30813218
- PMCID: PMC6408109
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014697
Early characteristics of fulminant myocarditis vs non-fulminant myocarditis: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Fulminant myocarditis (FM) is a sub-category myocarditis. Its primary characteristic is a rapidly progressive clinical course that necessitates hemodynamic support. FM can be difficult to predict at the onset of myocarditis. The aim of this meta-analysis was to identify the early characteristics in FM compared to those of non-fulminant myocarditis (NFM).
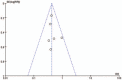
Methods: We searched the databases of MEDLINE, EMBASE, CENTRAL, for studies comparing FM with acute NFM from January 1, 2000 to June 1, 2018. The baseline variables were compared in each study. Mean differences (MD) and relative ratios (RR) were calculated.
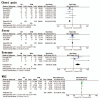
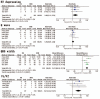
Results: Seven studies (158 FM patients and 388 NFM patients) were included in the analysis. The FM group had significantly lower systolic blood pressure (SBP), higher creatine kinase (CK), wider QRS duration, lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), thicker left ventricular posterior wall diameter (LVPWd), higher incidence of ST depression, ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation (Vt/Vf) and syncope, less incidence of chest pain than the NFM groups. There was no difference in terms of heart rate (HR), c-reactive protein (CRP), fever, dyspnea, white blood cells (WBC), atrioventricular block (AVB), Q waves, ST elevation, interventricular septum diameter (IVSd), or end-diastolic left ventricular diameter (LVEDd) between FM and NFM.
Conclusion: We found that the lower SBP, higher CK, wider QRS duration, lower LVEF, thicker LVPWd, higher incidence of ST depression, Vt/Vf and syncope as well as lower incidence of chest pain were early characteristics of FM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Characteristics of electrocardiogram in fulminant myocarditis].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 24;52(8):914-921. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20230821-00101. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39143783 Chinese.
-
Survival and Left Ventricular Function Changes in Fulminant Versus Nonfulminant Acute Myocarditis.Circulation. 2017 Aug 8;136(6):529-545. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.026386. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28576783
-
[Long term prognosis of fulminant myocarditis and predictors related to impaired cardiac function post discharge].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2022 Mar 24;50(3):263-269. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20211206-01056. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35340145 Chinese.
-
Fulminant Myocarditis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Dec 15;124(12):1954-1960. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31679645 Review.
-
COVID-19 and acute myocarditis: current literature review and diagnostic challenges.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020 Sep 21;66Suppl 2(Suppl 2):48-54. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.66.S2.48. eCollection 2020. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020. PMID: 32965356 Review.
Cited by
-
A fatal case of fulminant myocarditis after influenza infection with a rapidly progressive course: A case report.IDCases. 2024 May 12;36:e01986. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2024.e01986. eCollection 2024. IDCases. 2024. PMID: 38779145 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of Pulsed Field Ablation Versus Thermal Ablation for Pulmonary Vein Isolation in AF: A Broad Overview Focusing on Efficacy, Safety and Outcomes.Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev. 2024 Aug 22;13:e13. doi: 10.15420/aer.2024.05. eCollection 2024. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39221061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Symptomatic Young Adults with ST-Segment Elevation-Acute Coronary Syndrome or Myocarditis: The Three-Factor Diagnostic Model.J Clin Med. 2022 Feb 10;11(4):916. doi: 10.3390/jcm11040916. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35207189 Free PMC article.
-
Acute coronary syndrome versus acute myocarditis in young adults-value of speckle tracking echocardiography.PLoS One. 2022 Aug 8;17(8):e0271483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271483. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35939417 Free PMC article.
-
Successful rescue of fulminant myocarditis with mechanical circulatory support and immunosuppression therapy: A case report.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 19;10:1144630. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1144630. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37153457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karcic A, Conrad AR. Fulminant myocarditis. N Engl J Med 2000;343:299author reply 299-300. - PubMed
-
- Batra AS, Lewis AB. Acute myocarditis. Curr Opin Pediatr 2001;13:234–9. - PubMed
-
- Veronese G, Ammirati E, Cipriani M, et al. Not every fulminant lymphocytic myocarditis fully recovers. Eur Heart J 2017;38:1433. - PubMed
-
- Yang G, Jian D, Mingzi G, et al. The experience of successful therapy with ECMO on the patient diagnosed as fulminant myocarditis with multiple organ failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;70:C122.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

