Chemical Characterization and Antiplatelet Potential of Bioactive Extract from Tomato Pomace (Byproduct of Tomato Paste)
- PMID: 30813256
- PMCID: PMC6412684
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11020456
Chemical Characterization and Antiplatelet Potential of Bioactive Extract from Tomato Pomace (Byproduct of Tomato Paste)
Abstract
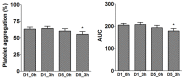
We examined the ability of tomato pomace extract (by-product) to affect platelet aggregation in healthy humans (clinical pilot study). In phase 1 the tolerance of participants (n = 15; 5 per dose level) ingesting tomato pomace extract across three dose levels (1, 2.5, and 10 g) was evaluated. Phase 2 was a single-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel design human (male, n = 99; 33 per group) pilot intervention trial investigating the acute and repeated dose effects (5 days) of different doses of tomato pomace extract (1 g, 2.5 g or placebo) on platelet aggregation ex vivo. Various flavonoids (coumaric acid, floridzin, floretin, procyanidin B₂, luteolin-7-O-glucoside, kaempferol, and quercitin) and nucleosides (adenosine, inosine, and guanosine) were identified in the tomato pomace extract. The clinical study showed that the daily consumption of 1 g of aqueous extract of tomato pomace for 5 days exerted an inhibitory activity on platelet aggregation.
Keywords: clinical pilot study; extract; platelet; tolerance; tomato pomace.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cuevas-Ramos D., Almeda-Valdes P., Chavez-Manzanera E., Meza-Arana C.E., Brito-Cordova G., Mehta R., Perez-Mendez O., Gomez-Perez F.J. Effect of tomato consumption on high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: a randomized, single-blinded, controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2013;6:263–273. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S48858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Valderas-Martinez P., Chiva-Blanch G., Casas R., Arranz S., Martinez-Huelamo M., Urpi-Sarda M., Torrado X., Corella D., Lamuela-Raventos R.M., Estruch R. Tomato sauce enriched with olive oil exerts greater effects on cardiovascular disease risk factors than raw tomato and tomato sauce: A randomized trial. Nutrients. 2016;8:170. doi: 10.3390/nu8030170. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

