What an Escherichia coli Mutant Can Teach Us About the Antibacterial Effect of Chlorophyllin
- PMID: 30813305
- PMCID: PMC6406390
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms7020059
What an Escherichia coli Mutant Can Teach Us About the Antibacterial Effect of Chlorophyllin
Abstract
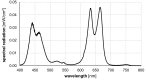
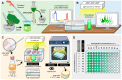
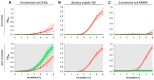
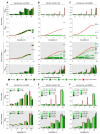
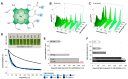
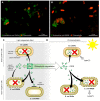
Due to the increasing development of antibiotic resistances in recent years, scientists search intensely for new methods to control bacteria. Photodynamic treatment with porphyrins such as chlorophyll derivatives is one of the most promising methods to handle bacterial infestation, but their use is dependent on illumination and they seem to be more effective against Gram-positive bacteria than against Gram-negatives. In this study, we tested chlorophyllin against three bacterial model strains, the Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis 168, the Gram-negative Escherichia coli DH5α and E. coli strain NR698 which has a deficient outer membrane, simulating a Gram-negative "without" its outer membrane. Illuminated with a standardized light intensity of 12 mW/cm², B. subtilis showed high sensitivity already at low chlorophyllin concentrations (≤10⁵ cfu/mL: ≤0.1 mg/L, 10⁶⁻10⁸ cfu/mL: 0.5 mg/L), whereas E. coli DH5α was less sensitive (≤10⁵ cfu/mL: 2.5 mg/L, 10⁶ cfu/mL: 5 mg/L, 10⁷⁻10⁸ cfu/mL: ineffective at ≤25 mg/L chlorophyllin). E. coli NR698 was almost as sensitive as B. subtilis against chlorophyllin, pointing out that the outer membrane plays a significant role in protection against photodynamic chlorophyllin impacts. Interestingly, E. coli NR698 and B. subtilis can also be inactivated by chlorophyllin in darkness, indicating a second, light-independent mode of action. Thus, chlorophyllin seems to be more than a photosensitizer, and a promising substance for the control of bacteria, which deserves further investigation.
Keywords: aPDT; alternative antibiotics; antimicrobial photodynamic therapy; chlorophyll; photosensitization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using Colistin as a Trojan Horse: Inactivation of Gram-Negative Bacteria with Chlorophyllin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Sep 20;8(4):158. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040158. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547053 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 7;11(10):1371. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101371. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290029 Free PMC article.
-
Photoinactivation effect of eosin methylene blue and chlorophyllin sodium-copper against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli.Lasers Med Sci. 2017 Jul;32(5):1081-1088. doi: 10.1007/s10103-017-2210-1. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Lasers Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28429192
-
Protochlorophyllide: a new photosensitizer for the photodynamic inactivation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Jan;290(2):156-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01413.x. Epub 2008 Nov 14. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19025572
-
Antibacterial photodynamic therapy: overview of a promising approach to fight antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.J Clin Transl Res. 2015 Dec 1;1(3):140-167. eCollection 2015 Dec 30. J Clin Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 30873451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using Colistin as a Trojan Horse: Inactivation of Gram-Negative Bacteria with Chlorophyllin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Sep 20;8(4):158. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8040158. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547053 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorophyllin Supplementation of Medicated or Unmedicated Swine Diets Impact on Fecal Escherichia coli and Enterococci.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;14(13):1955. doi: 10.3390/ani14131955. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998066 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethylenimine Increases Antibacterial Efficiency of Chlorophyllin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Oct 7;11(10):1371. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101371. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290029 Free PMC article.
-
Riboflavin- and chlorophyllin-based antimicrobial photoinactivation of Brevundimonas sp. ESA1 biofilms.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 21;12:1006723. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1006723. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36262183 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic Inactivation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by a Natural Food Colorant (E-141ii).Molecules. 2020 Sep 29;25(19):4464. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194464. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33003282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; Stockholm, Sweden: 2017. [(accessed on 31 December 2018)]. Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/documents/AMR-surveillance-Euro....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

