Selective Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase B by Acacetin 7-Methyl Ether Isolated from Turnera diffusa (Damiana)
- PMID: 30813423
- PMCID: PMC6412401
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24040810
Selective Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase B by Acacetin 7-Methyl Ether Isolated from Turnera diffusa (Damiana)
Abstract
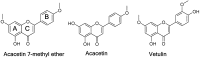
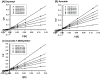
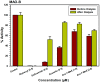
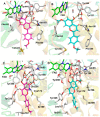
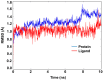
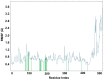
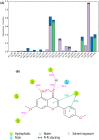
The investigation of the constituents that were isolated from Turnera diffusa (damiana) for their inhibitory activities against recombinant human monoamine oxidases (MAO-A and MAO-B) in vitro identified acacetin 7-methyl ether as a potent selective inhibitor of MAO-B (IC50 = 198 nM). Acacetin 7-methyl ether (also known as 5-hydroxy-4', 7-dimethoxyflavone) is a naturally occurring flavone that is present in many plants and vegetables. Acacetin 7-methyl ether was four-fold less potent as an inhibitor of MAO-B when compared to acacetin (IC50 = 50 nM). However, acacetin 7-methyl ether was >500-fold selective against MAO-B over MAO-A as compared to only two-fold selectivity shown by acacetin. Even though the IC50 for inhibition of MAO-B by acacetin 7-methyl ether was ~four-fold higher than that of the standard drug deprenyl (i.e., SelegilineTM or ZelaparTM, a selective MAO-B inhibitor), acacetin 7-methyl ether's selectivity for MAO-B over MAO-A inhibition was greater than that of deprenyl (>500- vs. 450-fold). The binding of acacetin 7-methyl ether to MAO-B was reversible and time-independent, as revealed by enzyme-inhibitor complex equilibrium dialysis assays. The investigation on the enzyme inhibition-kinetics analysis with varying concentrations of acacetin 7-methyl ether and the substrate (kynuramine) suggested a competitive mechanism of inhibition of MAO-B by acacetin 7-methyl ether with Ki value of 45 nM. The docking scores and binding-free energies of acacetin 7-methyl ether to the X-ray crystal structures of MAO-A and MAO-B confirmed the selectivity of binding of this molecule to MAO-B over MAO-A. In addition, molecular dynamics results also revealed that acacetin 7-methyl ether formed a stable and strong complex with MAO-B. The selective inhibition of MAO-B suggests further investigations on acacetin 7-methyl as a potential new drug lead for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Turnera diffusa; acacetin; acacetin 7-methyl ether; molecular docking; molecular dynamics; monoamine oxidase-A; monoamine oxidase-B; neurological disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Potent inhibitions of monoamine oxidase A and B by acacetin and its 7-O-(6-O-malonylglucoside) derivative from Agastache rugosa.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Nov;104(Pt A):547-553. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.06.076. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28634060
-
Isolation of Acacetin from Calea urticifolia with Inhibitory Properties against Human Monoamine Oxidase-A and -B.J Nat Prod. 2016 Oct 28;79(10):2538-2544. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00440. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Nat Prod. 2016. PMID: 27754693
-
The Benzopyrone Biochanin-A as a reversible, competitive, and selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitor.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 10;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1525-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28069007 Free PMC article.
-
Plant secondary metabolites- potent inhibitors of monoamine oxidase isoforms.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2014;14(1):28-33. doi: 10.2174/1871524914666140826111930. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25142815 Review.
-
The molecular pharmacology of L-deprenyl.Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 5;226(2):97-108. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90170-z. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1639115 Review.
Cited by
-
Selected Natural Products in Neuroprotective Strategies for Alzheimer's Disease-A Non-Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 21;23(3):1212. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031212. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular docking/dynamics simulations, MEP analysis, bioisosteric replacement and ADME/T prediction for identification of dual targets inhibitors of Parkinson's disease with novel scaffold.In Silico Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 19;11(1):3. doi: 10.1007/s40203-023-00139-3. eCollection 2023. In Silico Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36687301 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease: Unravelling the Medicinal Perspectives and Recent Developments of Heterocyclic Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2025;24(4):263-284. doi: 10.2174/0118715273340983241018095529. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 39501950 Review.
-
Computationally Assisted Lead Optimization of Novel Potent and Selective MAO-B Inhibitors.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 24;9(10):1304. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101304. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680421 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Interactions of O-Methylated Flavonoid Natural Products with Human Monoamine Oxidase-A and -B.Molecules. 2020 Nov 17;25(22):5358. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225358. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33212830 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

