Enhancement of Functionality and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cell-Based Therapy Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 30813471
- PMCID: PMC6412804
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20040982
Enhancement of Functionality and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cell-Based Therapy Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
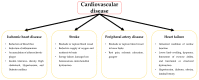
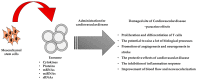
Cardiovascular disease usually triggers coronary heart disease, stroke, and ischemic diseases, thus promoting the development of functional failure. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are cells that can be isolated from various human tissues, with multipotent and immunomodulatory characteristics to help damaged tissue repair and avoidance of immune responses. Much research has proved the feasibility, safety, and efficiency of MSC-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Despite the fact that the precise mechanism of MSCs remains unclear, their therapeutic capability to treat ischemic diseases has been tested in phase I/II clinical trials. MSCs have the potential to become an effective therapeutic strategy for the treatment of ischemic and non-ischemic cardiovascular disorders. The molecular mechanism underlying the efficacy of MSCs in promoting engraftment and accelerating the functional recovery of injury sites is still unclear. It is hypothesized that the mechanisms of paracrine effects for the cardiac repair, optimization of the niche for cell survival, and cardiac remodeling by inflammatory control are involved in the interaction between MSCs and the damaged myocardial environment. This review focuses on recent experimental and clinical findings related to cardiovascular disease. We focus on MSCs, highlighting their roles in cardiovascular disease repair, differentiation, and MSC niche, and discuss their therapeutic efficacy and the current status of MSC-based cardiovascular disease therapies.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; exosome; mesenchymal stem cells; natural products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders of the grant had no role in the study design, data collection or analysis, the decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Writing C., Smith S.C., Jr., Collins A., Ferrari R., Holmes D.R., Jr., Logstrup S., McGhie D.V., Ralston J., Sacco R.L., Stam H., et al. Our time: A call to save preventable death from cardiovascular disease (heart disease and stroke) Glob. Heart. 2012;7:297–305. doi: 10.1016/j.gheart.2012.08.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources