Effect of Ramadan Fasting on Weight and Body Composition in Healthy Non-Athlete Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30813495
- PMCID: PMC6412279
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11020478
Effect of Ramadan Fasting on Weight and Body Composition in Healthy Non-Athlete Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Ramadan involves one month of fasting from sunrise to sunset. In this meta-analysis, we aimed to determine the effect of Ramadan fasting on weight and body composition.
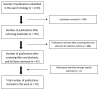
Methods: In May 2018, we searched six databases for publications that measured weight and body composition before and after Ramadan, and that did not attempt to influence physical activity or diet.
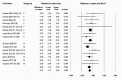
Results: Data were collected from 70 publications (90 comparison groups, 2947 participants). There was a significant positive correlation between starting body mass index and weight lost during the fasting period. Consistently, there was a significant reduction in fat percentage between pre-Ramadan and post-Ramadan in people with overweight or obesity (-1.46 (95% confidence interval: -2.57 to -0.35) %, p = 0.010), but not in those of normal weight (-0.41 (-1.45 to 0.63) %, p = 0.436). Loss of fat-free mass was also significant between pre-Ramadan and post-Ramadan, but was about 30% less than loss of absolute fat mass. At 2⁻5 weeks after the end of Ramadan, there was a return towards, or to, pre-Ramadan measurements in weight and body composition.
Conclusions: Even with no advice on lifestyle changes, there are consistent-albeit transient-reductions in weight and fat mass with the Ramadan fast, especially in people with overweight or obesity.
Keywords: Ramadan; body composition; body weight; intermittent fasting.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. A.S. has received payment from Eli Lilly, the Pharmacy Guild of Australia, Novo Nordisk, the Dietitians Association of Australia, Shoalhaven Family Medical Centres and the Pharmaceutical Society of Australia for seminar presentation at conferences, and served on the Nestlé Health Science Optifast® VLCDTM Advisory Board from 2016-2018. She is also the author of
Figures






References
-
- Kettani H. World Muslim Population: 1950–2020. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010;1:154–164.
-
- Sakr A.H. Fasting in Islam. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1975;67:17–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

