Low-Frequency Mutational Heterogeneity of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Subtypes: Information to Direct Precision Oncology
- PMID: 30813596
- PMCID: PMC6429455
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20051011
Low-Frequency Mutational Heterogeneity of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Subtypes: Information to Direct Precision Oncology
Abstract
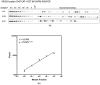
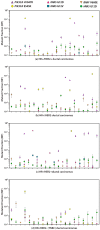
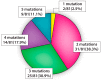
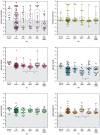
Information regarding the role of low-frequency hotspot cancer-driver mutations (CDMs) in breast carcinogenesis and therapeutic response is limited. Using the sensitive and quantitative Allele-specific Competitor Blocker PCR (ACB-PCR) approach, mutant fractions (MFs) of six CDMs (PIK3CA H1047R and E545K, KRAS G12D and G12V, HRAS G12D, and BRAF V600E) were quantified in invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs; including ~20 samples per subtype). Measurable levels (i.e., ≥ 1 × 10-5, the lowest ACB-PCR standard employed) of the PIK3CA H1047R, PIK3CA E545K, KRAS G12D, KRAS G12V, HRAS G12D, and BRAF V600E mutations were observed in 34/81 (42%), 29/81 (36%), 51/81 (63%), 9/81 (11%), 70/81 (86%), and 48/81 (59%) of IDCs, respectively. Correlation analysis using available clinicopathological information revealed that PIK3CA H1047R and BRAF V600E MFs correlate positively with maximum tumor dimension. Analysis of IDC subtypes revealed minor mutant subpopulations of critical genes in the MAP kinase pathway (KRAS, HRAS, and BRAF) were prevalent across IDC subtypes. Few triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) had appreciable levels of PIK3CA mutation, suggesting that individuals with TNBC may be less responsive to inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. These results suggest that low-frequency hotspot CDMs contribute significantly to the intertumoral and intratumoral genetic heterogeneity of IDCs, which has the potential to impact precision oncology approaches.
Keywords: PIK3CA; TNBC; breast cancer; cancer-driver; heterogeneity; invasive ductal carcinoma; mutation; subclonal; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Figures
References
-
- Hammond M.E., Hayes D.F., Dowsett M., Allred D.C., Hagerty K.L., Badve S., Fitzgibbons P.L., Francis G., Goldstein N.S., Hayes M., et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010;28:2784–2795. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wolff A.C., Hammond M.E., Hicks D.G., Dowsett M., McShane L.M., Allison K.H., Allred D.C., Bartlett J.M., Bilous M., Fitzgibbons P., et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:3997–4013. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.9984. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

