A high-throughput SNP discovery strategy for RNA-seq data
- PMID: 30813897
- PMCID: PMC6391812
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-019-5533-4
A high-throughput SNP discovery strategy for RNA-seq data
Abstract
Background: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) have been applied as important molecular markers in genetics and breeding studies. The rapid advance of next generation sequencing (NGS) provides a high-throughput means of SNP discovery. However, SNP development is limited by the availability of reliable SNP discovery methods. Especially, the optimum assembler and SNP caller for accurate SNP prediction from next generation sequencing data are not known.
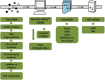
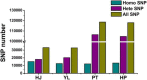
Results: Herein we performed SNP prediction based on RNA-seq data of peach and mandarin peel tissue under a comprehensive comparison of two paired-end read lengths (125 bp and 150 bp), five assemblers (Trinity, IDBA, oases, SOAPdenovo, Trans-abyss) and two SNP callers (GATK and GBS). The predicted SNPs were compared with the authentic SNPs identified via PCR amplification followed by gene cloning and sequencing procedures. A total of 40 and 240 authentic SNPs were presented in five anthocyanin biosynthesis related genes in peach and in nine carotenogenic genes in mandarin. Putative SNPs predicted from the same RNA-seq data with different strategies led to quite divergent results. The rate of false positive SNPs was significantly lower when the paired-end read length was 150 bp compared with 125 bp. Trinity was superior to the other four assemblers and GATK was substantially superior to GBS due to a low rate of missing authentic SNPs. The combination of assembler Trinity, SNP caller GATK, and the paired-end read length 150 bp had the best performance in SNP discovery with 100% accuracy both in peach and in mandarin cases. This strategy was applied to the characterization of SNPs in peach and mandarin transcriptomes.
Conclusions: Through comparison of authentic SNPs obtained by PCR cloning strategy and putative SNPs predicted from different combinations of five assemblers, two SNP callers, and two paired-end read lengths, we provided a reliable and efficient strategy, Trinity-GATK with 150 bp paired-end read length, for SNP discovery from RNA-seq data. This strategy discovered SNP at 100% accuracy in peach and mandarin cases and might be applicable to a wide range of plants and other organisms.
Keywords: GATK; Paired-end read length; RNA-seq; Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP); Trinity.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Jehan T, Lakhanpaul S. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) – methods and applications in plant genetics: a review. Indian J Biotechnol. 2006;5:435–459.
-
- Hiremath PJ, Kumar A, Penmetsa RV, Farmer A, Schlueter JA, Chamarthi SK, Whaley AM, Carrasquilla-Garcia N, Gaur PM, Upadhyaya HD, et al. Large-scale development of cost-effective SNP marker assays for diversity assessment and genetic mapping in chickpea and comparative mapping in legumes. Plant Biotechnol J. 2012;10(6):1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2012.00710.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

