Area-level deprivation and preterm birth: results from a national, commercially-insured population
- PMID: 30813938
- PMCID: PMC6391769
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-019-6533-7
Area-level deprivation and preterm birth: results from a national, commercially-insured population
Abstract
Background: Area-level deprivation is associated with multiple adverse birth outcomes. Few studies have examined the mediating pathways through which area-level deprivation affects these outcomes. The objective of this study was to investigate the association between area-level deprivation and preterm birth, and examine the mediating effects of maternal medical, behavioural, and psychosocial factors.
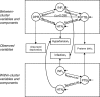
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using national, commercial health insurance claims data from 2011, obtained from the Health Care Cost Institute. Area-level deprivation was derived from principal components methods using ZIP code-level data. Multilevel structural equation modeling was used to examine mediating effects.
Results: In total, 138,487 women with a live singleton birth residing in 14,577 ZIP codes throughout the United States were included. Overall, 5.7% of women had a preterm birth. In fully adjusted generalized estimation equation models, compared to women in the lowest quartile of area-level deprivation, odds of preterm birth increased by 9.6% among women in the second highest quartile (odds ratio (OR) 1.096; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.021, 1.176), by 11.3% in the third highest quartile (OR 1.113; 95% CI 1.035, 1.195), and by 24.9% in the highest quartile (OR 1.249; 95% CI 1.165, 1.339). Hypertension and infection moderately mediated this association.
Conclusions: Even among commercially-insured women, area-level deprivation was associated with increased risk of preterm birth. Similar to individual socioeconomic status, area-level deprivation does not have a threshold effect. Implementation of policies to reduce area-level deprivation, and the screening and treatment of maternal mediators may be associated with a lower risk of preterm birth.
Keywords: Area-level deprivation; Commercially-insured; Mediating pathways; Preterm birth.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Data are compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, therefore this study was exempt from review by Institutional Review Boards.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJ, Curtin SC, Matthews TJ. Births: final data for 2013. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2015;64(1):1–65. - PubMed
-
- Mathews TJ, MacDorman MF, Thoma ME. Infant mortality statistics from the 2013 period linked birth/infant death data set. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2015;64(9):1–30. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine . Preterm birth: causes, consequences, and prevention. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2007. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

