Taking connected mobile-health diagnostics of infectious diseases to the field
- PMID: 30814711
- PMCID: PMC6776470
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-0956-2
Taking connected mobile-health diagnostics of infectious diseases to the field
Abstract
Mobile health, or 'mHealth', is the application of mobile devices, their components and related technologies to healthcare. It is already improving patients' access to treatment and advice. Now, in combination with internet-connected diagnostic devices, it offers novel ways to diagnose, track and control infectious diseases and to improve the efficiency of the health system. Here we examine the promise of these technologies and discuss the challenges in realizing their potential to increase patients' access to testing, aid in their treatment and improve the capability of public health authorities to monitor outbreaks, implement response strategies and assess the impact of interventions across the world.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
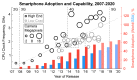
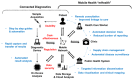
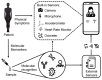

References
-
- GSMA. The Mobile Economy. 2017 https://www.gsma.com/mobileeconomy.
-
- GSMA. Mobile Economy Sub-Saharan Africa. 2014 https://www.gsma.com/mobileeconomy/archive/GSMA_ME_SubSaharanAfrica_2014.
-
- Perkel JM. Pocket laboratories. Nature. 2017;545:119–121. - PubMed
-
- GSMA. Global Mobile Trends. 2017 https://www.gsma.com/globalmobiletrends/index.html.
-
- Ginsburg GS, Willard HF. Genomic and Personalized Medicine. Vol. 1 Elsevier/Academic Press; Cambridge: 2013.

