Production and characterization of polyclonal antibodies to human recombinant domain B-free antihemophilic factor VIII
- PMID: 30814851
- PMCID: PMC6353303
- DOI: 10.3906/biy-1704-10
Production and characterization of polyclonal antibodies to human recombinant domain B-free antihemophilic factor VIII
Abstract
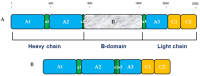
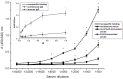
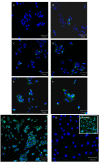
Moroctocog alpha is a human B-domain deleted recombinant factor VIII (BDDrFVIII), which represents a new generation of pure antihemophilic products. We describe here an optimized procedure for polyclonal anti-FVIII-antibody production with the use of BDDrFVIII as an immunogen. The main immunochemical characteristics of the produced antibodies and their potential biomedical applications are also reported. Rabbits were immunized with BDDrFVIII as an emulsion with Freund's adjuvant or with antigen immobilized in polyacrylamide gel (PAAG). Antibody titers in immune sera were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). IgG purification was performed by afine chromatography on protein A-sepharose. Immune sera and IgG were tested by immunoblotting with the use of human plasma of healthy donors and people with hemophilia A, platelet lysates, and commercial plasma-derived concentrates as sources of FVIII-related antigens. FVIII-producing human umbilical vein cells were processed for immunocytochemical staining with the use of purified anti-FVIII-antibodies. Immunization of rabbits with PAAG-trapped antigen induced more potent immune response compared to the standard immunization procedure with Freund's adjuvant. The lowest working amount of immune IgG, measured by ELISA, was ~50 ng. Immunoblotting demonstrated that anti-BDDrFVIII antibodies effectively recognize the whole FVIII molecule (320 kDa), as well as different truncated polypeptides thereof, and are suitable for immunocytochemical analysis of FVIII-producing cells. An optimized procedure for the production of polyclonal antibodies against FVIII with the use of PAAG-immobilized BDDrFVIII (moroctocog alpha) was proposed and successfully validated. The produced antibodies are suitable for detecting and measuring FVIII-related antigens and may have various biomedical applications.
Keywords: B-Domain deleted recombinant factor VIII (moroctocog alpha); antibody production; hemophilia A; plasma-derived FVIII products; platelets.
Figures



References
-
- Amero SA , James TC , Elgin SC ( 1988. ). Production of antibodies using proteins in gel bands . Methods Mol Biol 3 : 355 - 362 . - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM ( 1976. ). Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding . Anal Biochem 72 : 248 - 254 . - PubMed
-
- Chandler WL , Ferrell C , Lee J , Tun T , Kha H ( 2003. ). Comparison of three methods for measuring factor VIII levels in plasma . Am J Clin Pathol 120 : 34 - 39 . - PubMed
-
- Chitlur M , Young G ( 2016. ). Global assays in hemophilia . Semin Hematol 53 : 40 - 45 . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
