Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: Association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission
- PMID: 30815171
- PMCID: PMC6371318
Retrospective analysis of health claims to evaluate pharmacotherapies with potential for repurposing: Association of bupropion and stimulant use disorder remission
Abstract
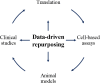
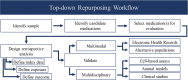
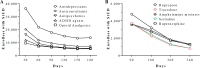
Drug repurposing is the identification of novel indication(s) for existing medications. Health claims data provide a burgeoning resource to evaluate pharmacotherapies with repurposing potential. To demonstrate a workflow for drug repurposing using claims data, we assessed the association between prescription of bupropion and stimulant use disorder (StUD) remission. Using the Truven Marketscan database, 96,156 individuals with a StUD were identified. Logistic regression was used to model the association between new bupropion prescriptions and remission while controlling for age, sex, region, StUD severity, antidepressant co-prescriptions, and comorbid mood and attention disorders. Prescription of bupropion within 30 days offirst documented StUD diagnosis increased odds of a subsequent remission diagnosis by 2.1 times (99% confidence interval: 1.09-3.89) in individuals with an amphetamine use disorder, but not those with a cocaine use disorder. This work provides a framework for reverse-translational drug repurposing, which may be applied to many other medical conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Ashburn TT, Thor KB. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:673–83. - PubMed
-
- Hoehndorf R, Oellrich A, Rebholz-Schuhmann D, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV. 2012. Linking PharmGKB to phenotype studies and animal models of disease for drug repurposing. Pac Symp Biocomput; pp. 388–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
