Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng modulate T cell function via the regulation of NF-AT-mediated IL-2 production
- PMID: 30815315
- PMCID: PMC6365338
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-018-0428-8
Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng modulate T cell function via the regulation of NF-AT-mediated IL-2 production
Abstract
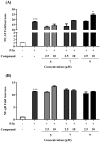
Korean red ginseng is a traditional health food frequently used to prevent or treat various diseases worldwide. In this study, we evaluated the immunomodulatory activities of eleven compounds (1-11) isolated from Korean red ginseng, focusing on T cell function. First, the effects of the eleven compounds were studied on the regulation of IL-2, a potent T cell growth factor. Compounds 5, 7, and 9 significantly increased IL-2 secretion in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)/ionomycin (Io)-induced EL-4 T cells. Next, we examined the effects of compounds 5, 7, and 9 on the regulation of transcription factors related to IL-2 production in T cells. Compound 9 significantly increased the PMA/Io-induced promoter activity of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-AT) in EL-4 T cells, but did not have any significant effects on the promoters of NF- κB. These results suggest that compound 9 activates T cell function via the regulation of NF-AT-mediated IL-2 production.
Keywords: Ginsenosides; IL-2; Korean red ginseng; Panax ginseng.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Chen F, Sun Y, Zheng SL, Qin Y, McClements DJ, Hu JN, Deng ZY. Antitumor and immunomodulatory effects of ginsenoside Rh2 and its octyl ester derivative in H22 tumor-bearing mice. J Funct Foods. 2017;32:382–390. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.03.013. - DOI
-
- He LX, Ren JW, Liu R, Chen QH, Zhao J, Wu X, Zhang ZF, Wang JB, Pettinato G, Li Y. Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) oligopeptides regulate innate and adaptive immune responses in mice via increased macrophage phagocytosis capacity, NK cell activity and Th cells secretion. Food Funct. 2017;8:3523–3532. doi: 10.1039/C7FO00957G. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
