Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with FGF19 Amplification Assessed by Fluorescence in situ Hybridization: A Large Cohort Study
- PMID: 30815392
- PMCID: PMC6388559
- DOI: 10.1159/000488541
Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with FGF19 Amplification Assessed by Fluorescence in situ Hybridization: A Large Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: FGF19 amplification is a relatively novel type of genetic aberration that has been proposed to be a driver of hepatocarcinogenesis. Selective inhibitors of FGFR4, a receptor of FGF19, have been developed as targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Despite the role of FGF19 in mediating HCC progression, the clinicopathological characterization of patients exhibiting FGF19 amplification remains unclear. Immunohistochemical staining is the simplest and most widely used method of identifying aberrations in the FGF19 gene, although its specificity is very low.
Methods: This study investigated the prognostic significance of FGF19 amplification in a large cohort of 989 HCC patients using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), which has a high degree of specificity. In addition, FISH data from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections were compared with copy number variation (CNV) data obtained from fresh frozen sections to validate the use of FISH as a diagnostic tool.
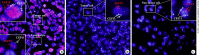
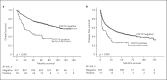
Results: FGF19 amplifications were detected by FISH in 51 (5.15%) of the 989 patients, and were independently associated with poor survival and a higher risk of tumor recurrence, as well as with poor prognostic factors such as a high α-fetoprotein level, hepatitis B or C virus infection, a large tumor size, microvascular invasion, and necrosis. In addition, FGF19 amplification was associated with TP53 mutation, and was mutually exclusive with CTNNB1 mutation. The results of the FISH and CNV analyses exhibited a significant concordance rate of 96% (κ = 0.618, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: These data indicate that FGF19 amplification represents a unique molecular subtype associated with poor prognostic characteristics, which supports the hypothesis that the FGF19-FGFR4 signaling pathway plays an important role in hepatocarcinogenesis. We have also demonstrated that FISH is a viable alternative to CNV analysis, offering a number of advantages in the clinical setting.
Keywords: FGF19; Fluorescence in situ hybridization; Hepatocellular carcinoma; High copy number amplification; Prognosis.
Figures


References
-
- Torrecilla S, Llovet JM. New molecular therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2015;39((suppl 1)):S80–S85. - PubMed
-
- Guichard C, Amaddeo G, Imbeaud S, Ladeiro Y, Pelletier L, Maad IB, Calderaro J, Bioulac-Sage P, Letexier M, Degos F, Clément B, Balabaud C, Chevet E, Laurent A, Couchy G, Letouzé E, Calvo F, Zucman-Rossi J. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2012;44:694–698. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hagel M, Miduturu C, Sheets M, Rubin N, Weng W, Stransky N, Bifulco N, Kim JL, Hodous B, Brooijmans N, Shutes A, Winter C, Lengauer C, Kohl NE, Guzi T. First selective small molecule inhibitor of FGFR4 for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas with an activated FGFR4 signaling pathway. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:424–437. - PubMed
-
- Kaibori M, Sakai K, Ishizaki M, Matsushima H, De Velasco MA, Matsui K, Iida H, Kitade H, Kwon AH, Nagano H, Wada H, Haji S, Tsukamoto T, Kanazawa A, Takeda Y, Takemura S, Kubo S, Nishio K. Increased FGF19 copy number is frequently detected in hepatocellular carcinoma with a complete response after sorafenib treatment. Oncotarget. 2016;7:49091–49098. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

