The Incidence and Predisposing Factors of John Cunningham Virus-Induced Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in Southern Finland: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 30815501
- PMCID: PMC6386113
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofz024
The Incidence and Predisposing Factors of John Cunningham Virus-Induced Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in Southern Finland: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence, incidence rate (IR), predisposing factors, survival rate, and diagnostic delay of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) across medical specialties. Another objective was to survey how PML diagnosis was made in the studied cases.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional retrospective observational study of PML cases across different medical specialties during 2004-2016 in the Finnish Capital Region and Southern Finland. Data were obtained from clinical records, clinical microbiology, pathology and radiology department records, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) quality register medical records.
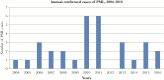
Results: A total of 31 patients were diagnosed with PML. The prevalence of PML was 1.56 per 100 000 people and the IR was 0.12 per 100 000 individuals per year during 2004-2016. Hematologic malignancies (n = 19) and HIV/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (n = 5) were the most common underlying diseases, and all patients who had malignant diseases had received cancer treatment. Before PML diagnosis, 21 (67.7%) patients were treated with chemotherapy, 14 (45.2%) patients with rituximab, and 1 patient (3.2%) with natalizumab. Two patients (6.5%) had no obvious immunocompromising disease or treatment. Neither gender, age, first symptoms, previous medication, nor underlying disease influenced the survival of PML patients significantly. The 5-year survival rate was poor, at less than 10%.
Conclusions: The majority of PML patients in our study had a predisposing disease or had immunosuppressive or monoclonal antibody therapy. In the future, broader use of immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory medications may increase incidence of PML among patients with diseases unassociated with PML. Safety screening protocols for John Cunningham virus and PML are important to prevent new PML cases.
Keywords: HIV; JC virus; monoclonal antibodies; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; rituximab.
Figures
References
-
- Gheuens S, Wüthrich C, Koralnik IJ. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: why gray and white matter. Annu Rev Pathol 2013; 8:189–215. - PubMed
-
- Eng PM, Turnbull BR, Cook SF, et al. . Characteristics and antecedents of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in an insured population. Neurology 2006; 67:884–6. - PubMed
-
- Palazzo E, Yahia SA. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in autoimmune diseases. Joint Bone Spine 2012; 79:351–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources