Genotyping of Candida albicans isolated from animals using 25S ribosomal DNA and ALT repeats polymorphism in repetitive sequence
- PMID: 30815612
- PMCID: PMC6386504
- DOI: 10.18502/cmm.4.4.381
Genotyping of Candida albicans isolated from animals using 25S ribosomal DNA and ALT repeats polymorphism in repetitive sequence
Abstract
Background and purpose: Candida albicans is the most prevalent Candida species isolated from animals. Candidiasis can be systemic in animals or may affect a single organ, such as the mouth, urinary tract, and skin. The aim of the present study was to determine the genetic diversity of C. albicans isolated from different animals and investigate the presence of a relationship between host specificity and genetic typing of C. albicans.
Materials and methods: For the purpose of the study, DNA extraction was performed on 27 clinical isolates of C. albicans obtained from animals. Subsequently, they were subjected to 25S ribosomal DNA amplification and ALT repeats in repetitive sequences (RPSs). The minimum inhibitory concentrations of fluconazole, ketoconazole, clotrimazole, nystatin, amphotericin B, and caspofungin were determined using the microdilution method based on the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute M27-S4 standard.
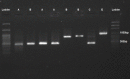
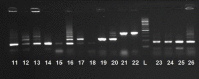
Results: Out of 27 C. albicans strains, 11, 6, 5, and 5 cases were recognized as genotypes A (40.8%), E (22.2%), B (18.5%), and C (18.5%), respectively, through amplification using AS-I, which revealed 17 different types of C. albicans. By combining the two typing methods, 27 C. albicans strains were finally divided into 22 genotypes.
Conclusion: Different genotypes showed genetic diversity among the C. albicans strains isolated from animal sources. The results revealed no special genotype relationship according to the host, anatomical source of isolation, and antifungal susceptibility.
Keywords: Animal; Antifungals; Candida albicans; Genotyping; Repetitive sequences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genotyping of Candida albicans on the basis of polymorphisms of ALT repeats in the repetitive sequence (RPS).J Dermatol Sci. 2006 Jan;41(1):43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2005.08.010. Epub 2005 Dec 20. J Dermatol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16364601
-
Virulence and antifungal susceptibility of microsatellite genotypes of Candida albicans from superficial and deep locations.Yeast. 2019 May;36(5):363-373. doi: 10.1002/yea.3397. Yeast. 2019. PMID: 31037772 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype analysis of Candida albicans isolates obtained from different body locations of patients with superficial candidiasis using PCRs targeting 25S rDNA and ALT repeat sequences of the RPS.J Dermatol Sci. 2006 Apr;42(1):31-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2005.12.003. Epub 2006 Jan 18. J Dermatol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16414246
-
Genotypes analysis and antifungal susceptibility of Candida albicans strains isolated from women with vaginal candidiasis in Jordan using PCR targeting 25SrDNA and ALT repeat sequences of the RPS.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Sep;40(8):1619-1624. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.8.9811. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39281223 Free PMC article.
-
Candida and candidaemia. Susceptibility and epidemiology.Dan Med J. 2013 Nov;60(11):B4698. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24192246 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Candida albicans Isolates from Mexican Women with Vulvovaginitis.J Fungi (Basel). 2025 May 2;11(5):354. doi: 10.3390/jof11050354. J Fungi (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422688 Free PMC article.
-
ABC typing and extracellular enzyme production of Candida albicans isolated from Candida vulvovaginitis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Jan;36(1):e24117. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24117. Epub 2021 Nov 27. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 34837715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sardi JC, Scorzoni L, Bernardi T, Fusco-Almeida AM, Mendes Giannini MJ. Candida species: current epidemiology, pathogenicity, biofilm formation, natural antifungal products and new therapeutic options. J Med Microbiol. 2013;62(Pt 1):10–24. - PubMed
-
- Odds FC. Molecular phylogenetics and epidemiology of Candida albicans. Future Microbiol. 2010;5(1):67–79. - PubMed
-
- Afsarian MH, Badali H, Boekhout T, Shokohi T, Katiraee F. Multilocus sequence typing of Candida albicans isolates from a burn intensive care unit in Iran. J Med Microbiol. 2015;64(Pt 3):248–53. - PubMed
-
- Verma RS, Rahman LU, Chanotiya CS, Verma RK, Chauhan A, Yadav A, et al. Essential oil composition of Lavandula angustifolia Mill cultivated in the mid hills of Uttarakhand, India. J Serbian Chem Soc. 2010;75(3):343–8.
-
- Sahana K, Nagarajan S, Rao L. London: Academic Press; 2011. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L) seed volatile oil: chemistry and role in health and disease Nuts and seeds in health and disease prevention; pp. 417–27.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
