Effects of secondary metabolites produced by different cyanobacterial populations on the freshwater zooplankters Brachionus calyciflorus and Daphnia pulex
- PMID: 30815809
- PMCID: PMC6476996
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-019-04543-1
Effects of secondary metabolites produced by different cyanobacterial populations on the freshwater zooplankters Brachionus calyciflorus and Daphnia pulex
Abstract
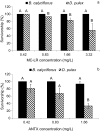
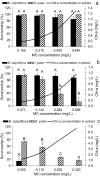
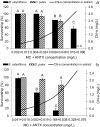
Cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic water bodies are a worldwide problem. Combined effects of mixtures of secondary metabolites produced by different cyanobacterial species on aquatic fauna are still not well recognised. We compared the survivorship of Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas (Rotifera) and Daphnia pulex Leyding (Cladocera) exposed to pure microcystin LR (MC-LR), anatoxin-a (ANTX) and to five extracts obtained from bloom-forming cyanobacteria Microcystis, Planktothrix and Dolichospermum. The obtained results revealed different response of the organisms to high concentrations of pure MC-LR, ANTX and complex cyanobacterial extracts. The extracts' toxicity to invertebrates was higher than that exerted by pure cyanotoxins and was dependent on the composition of cyanobacterial metabolites: Microcystis spp. extract containing anabaenopeptins A and B, aeruginosamide, four variants of cyanopeptolins and five MCs was not toxic to either of the organisms, whereas Planktothrix agardhii extract (I), containing anabaenopeptins A, B, F, 915, oscillamide Y, five different aeruginosins and four variants of MC was more toxic to daphnids than to rotifers. The extracts of another P. agarhdii (II) biomass and two different biomass samples of Dolichospermum spp. also affected survivorship of the rotifer and cladoceran, however, to various extent. It strongly suggests that non-ribosomal oligopeptides, other than MCs, had essential contribution to the observed toxicity to invertebrates and their effects on particular species or populations can vary depending on the secondary metabolite profiles of cyanobacteria.
Keywords: Anabaenopeptins; Anatoxin-a; Cyanopeptolins; Microcystins; Zooplankton.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- PN-ISO 10260 (2002) Water quality. Measurement of biochemical parameters. Spectrophotometric determination of chlorophyll-a. PWN Warszawa (in Polish)
-
- Baumann HI, Jüttner F. Inter-annual stability of oligopeptide patterns of Planktothrix rubescens blooms and mass mortality of Daphnia in Lake Hallwilersee. Limnologica. 2008;38:350–359. doi: 10.1016/j.limno.2008.05.010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

