A prospective randomized trial of a potassium competitive acid blocker vs proton pump inhibitors on the effect of ulcer healing after endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric neoplasia
- PMID: 30816056
- PMCID: PMC6460617
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060519828514
A prospective randomized trial of a potassium competitive acid blocker vs proton pump inhibitors on the effect of ulcer healing after endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric neoplasia
Abstract
Background/aims: Vonoprazan is a new a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) that was recently developed in Japan. However, vonoprazan's efficacy in healing gastric ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) remains controversial. This study aimed to compare the efficacy of P-CABs and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) in healing post-ESD ulcers.
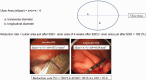
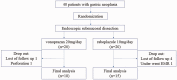
Materials and methods: This prospective randomized controlled trial (UMIN000017386) enrolled 40 patients with gastric neoplasia, who underwent ESD at our hospital from April 2015 to January 2016. Before ESD, patients were randomly divided into the following two groups: group V, vonoprazan 20 mg/day; or group R, rabeprazole 10 mg/day. Medications were taken 1 day before to 4 weeks after ESD. The ESD-induced artificial ulcer size was measured just after ESD and 4 weeks after ESD to calculate the reduction rate as follows: (ulcer area 4 weeks after ESD)/(ulcer area just after ESD) × 100.
Results: Eighteen patients in group V and 15 patients in group R were analyzed. The mean reduction rate was significantly different in groups V and R (93.3% vs 96.6%, respectively). Post-ESD bleeding was observed in two patients in group R and drug-induced hepatic injury in one patient in group R.
Conclusion: Rabeprazole facilitated the healing process post-ESD.
Keywords: Endoscopic submucosal dissection; artificial gastric ulcer; gastric neoplasia; rabeprazole; reduction rate; vonoprazan.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vonoprazan is superior to proton pump inhibitors in healing artificial ulcers of the stomach post-endoscopic submucosal dissection: A propensity score-matching analysis.Dig Endosc. 2017 Jan;29(1):57-64. doi: 10.1111/den.12705. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Dig Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27492962
-
Effect of vonoprazan on the treatment of artificial gastric ulcers after endoscopic submucosal dissection: Prospective randomized controlled trial.Dig Endosc. 2017 Jul;29(5):576-583. doi: 10.1111/den.12857. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Dig Endosc. 2017. PMID: 28267236 Clinical Trial.
-
Vonoprazan prevents bleeding from endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced gastric ulcers.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;44(6):583-91. doi: 10.1111/apt.13747. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27464849 Clinical Trial.
-
Vonoprazan versus proton-pump inhibitors for gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Dec;30(12):1416-1421. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001204. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29985791
-
Comparative efficacy of various anti-ulcer medications after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Surg Endosc. 2019 Apr;33(4):1271-1283. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6409-4. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Surg Endosc. 2019. PMID: 30167955
Cited by
-
Vonoprazan or Proton Pump Inhibitor for Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Patients Taking Antithrombotic Agents.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Aug;40(8):1890-1898. doi: 10.1111/jgh.17027. Epub 2025 May 27. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40420803 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Using proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of hepato-biliary-pancreatic cancer. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 14;13:979215. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.979215. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188583 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine2-Receptor Antagonists, Proton Pump Inhibitors, or Potassium-Competitive Acid Blockers Preventing Delayed Bleeding After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 19;10:1055. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01055. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31607912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of vonoprazan and proton pump inhibitors for the treatment of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 15;24(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03198-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38491413 Free PMC article.
-
The value of oral contrast-enhanced gastric ultrasonography in the diagnosis and staging of benign peptic ulcer.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 29;14(1):17390. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68430-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39075113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gotoda T, Kondo H, Ono H, et al. A new endoscopic mucosal resection procedure using an insulation-tipped electrosurgical knife for rectal flat lesions: report of two cases. Gastrointest Endosc 1999; 50: 560–563. - PubMed
-
- Ono H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Chin J Dig Dis 2005; 6: 119–121. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, Ogata S, Kawazoe S, et al. Clinical outcomes of EMR for gastric tumors: historical pilot evaluation between endoscopic submucosal dissection and conventional mucosal resection. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 63: 776–782. - PubMed
-
- Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Nakamura M, et al. Successful outcomes of a novel endoscopic treatment for GI tumors: endoscopic submucosal dissection with a mixture of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and sugar. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 63: 243–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous