Elevated red cell distribution width to platelet count ratio predicts poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer
- PMID: 30816333
- PMCID: PMC6395769
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40024-8
Elevated red cell distribution width to platelet count ratio predicts poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer
Abstract
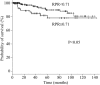
Red cell distribution width (RDW) to platelet ratio (RPR) is a prognosticator in acute pancreatitis and myocardial infarction; however, the prognostic values of RDW and RPR in breast cancer have not been studied. This retrospective analysis of 299 breast cancer patients investigated the association between RDW and RPR and clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis, compared to platelet distribution width to platelet count ratio (PDW/P) which is a known independent prognostic factor in patients with breast cancer. We found a significant correlation between RPR, and age and HER2 status. An elevated RPR significantly correlated with age and HER2 status. After a median follow-up duration of 48 months, tumour size, nuclear grade, PDW/P, and RPR were recgnized to be significantly associated with lower disease-free survival rates (tumour size: p < 0.01; nuclear grade, PDW/P, and RPR: p < 0.05) in univariate analysis. Tumour size and RPR were significant prognostic factors for lower disease-free survival rates, with hazard ratios of 4.31 (95% confidence interval: 1.76-10.53) (p < 0.01)] and 2.79 [95% confidence interval: 1.01-87.69) (p < 0.05)], respectively, in a multivariate analysis using the Cox proportional hazards model. This is the first study showing that an elevated RPR could independently predict poor prognosis in patients with breast carcinoma. Thus, RPR could be a novel biomarker for prognostic estimation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of red blood cell distribution width, platelet distribution width, and red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio in children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Sep;35(9):e23909. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23909. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 34273201 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Platelet Distribution Width-to-Plateletcrit Ratio as a Prognostic Marker for Patients With Breast Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2020 Jul;40(7):3947-3952. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14386. Anticancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32620636
-
The prognostic impact of the platelet distribution width-to-platelet count ratio in patients with breast cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 7;12(12):e0189166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189166. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29216259 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic effect of red cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio in colorectal cancer according to tumor stage and localization.J Cancer Res Ther. 2019 Jan-Mar;15(1):54-60. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_624_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30880755
-
Red blood cell distribution width and platelet counts are independent prognostic factors and improve the predictive ability of IPI score in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 11;19(1):1084. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6281-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31711453 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Red Blood Cell Distribution Width to Platelet Count Ratio Facilitates Preoperative Prediction of Recurrence in Surgically Treated Chronic Subdural Hematoma.Front Neurol. 2022 May 11;13:884231. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.884231. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35645986 Free PMC article.
-
The First Comprehensive Evaluation of Immuno-Inflammatory Markers for Prognosis in Esophageal Cancer Patients: A South Asian Perspective.Clin Pract. 2024 Oct 6;14(5):2071-2079. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14050163. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39451878 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the treatment efficacy and prognostic factors of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors for advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a multicenter, retrospective clinical study.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 24;15:1468342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1468342. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39512347 Free PMC article.
-
Red Cell Distribution Width to Platelet Ratio Is Associated with Increasing In-Hospital Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Kidney Injury.Dis Markers. 2022 Jan 17;2022:4802702. doi: 10.1155/2022/4802702. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35082929 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor educated platelet: the novel BioSource for cancer detection.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 May 11;23(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02927-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37170255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lippi G, Salvagno GL, Guidi GC. Red blood cell distribution width is significantly associated with aging and gender. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014;52:e197–e199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous