Chlorophyllin e6‑mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells
- PMID: 30816498
- PMCID: PMC6412394
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2019.7013
Chlorophyllin e6‑mediated photodynamic therapy inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells
Abstract
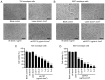
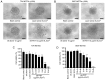
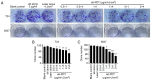
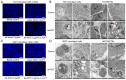
Patients with non‑muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) frequently relapse following surgery due to incomplete resection and chemoresistance, highlighting the importance of developing novel therapeutic strategies that mechanistically assist in eradicating the residual tumor. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the anticancer effect of chlorophyllin e6‑mediated photodynamic therapy (e6‑PDT) and its potential mechanisms by using monolayer cells or multicellular tumor spheroid models of human bladder cancer cells (T24 and 5637). The results revealed that e6‑PDT exhibited significant cytotoxicity in the T24 and 5637 cells of these two models as detected by the Water‑Soluble Tetrazolium Salts‑1 and CellTiter‑Glo Luminescent Cell Viability assays, respectively. Cell migration and invasion capacities decreased markedly following e6‑PDT. In addition, the cells following e6‑PDT exhibited typical morphological changes of apoptosis as detected by fluorescence microscopy with 4',6‑diamidino‑2‑phenylindole staining and transmission electron microscopy. A greater number of apoptotic cells were observed post‑e6‑PDT by flow cytometry. The expression levels of poly(adenosine diphosphate‑ribose) polymerase (PARP) and B‑cell lymphoma 2 protein were decreased, while cleaved PARP was increased, significantly following e6‑PDT as determined by western blotting. The level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) was increased, while the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) was decreased, significantly in e6‑PDT‑treated cells. Thus, the novel e6‑PDT exhibits prominent photo‑cytotoxicity effect and the induction of apoptosis was probably due to the inhibition of SOD activity and the generation of ROS. These results indicate that chlorophyllin e6 is an effective photosensitizer and that e6‑PDT may have a therapeutic application for the treatment of bladder cancer.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Photodynamic therapy with the novel photosensitizer chlorophyllin f induces apoptosis and autophagy in human bladder cancer cells.Lasers Surg Med. 2014 Apr;46(4):319-34. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22225. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Lasers Surg Med. 2014. PMID: 24464873
-
Chlorophyllin e4 is a novel photosensitizer against human bladder cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 May;27(5):1455-60. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.1656. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22294235
-
Autophagy inhibition sensitizes bladder cancer cells to the photodynamic effects of the novel photosensitizer chlorophyllin e4.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014 Apr 5;133:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 27. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2014. PMID: 24650577
-
Preparation of photo-controlled release ROS-responsive Ce6/elemene co-loaded liposomes and study on the effect on enhancing apoptosis of NMIBC.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Oct;179:117398. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117398. Epub 2024 Sep 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39245000
-
Nanotechnology in bladder cancer: current state of development and clinical practice.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(7):1189-201. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.212. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25929573 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Health Benefits through Chlorophylls and Chlorophyll-Rich Agro-Food: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2023 Jul 11;28(14):5344. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145344. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers containing pheophytins derived from Cnidoscolus quercifolius Pohl for photodynamic therapy against breast cancer: isolation, identification, characterization, in vitro activity, and in silico studies.Lasers Med Sci. 2025 Apr 4;40(1):175. doi: 10.1007/s10103-025-04431-w. Lasers Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40180629
-
The synthesis of novel water-soluble zinc (II) phthalocyanine based photosensitizers and exploring of photodynamic therapy activities on the PC3 cancer cell line.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2023 Sep;22(9):2037-2053. doi: 10.1007/s43630-023-00428-y. Epub 2023 May 11. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37166570
-
Accelerating skin regeneration and wound healing by controlled ROS from photodynamic treatment.Inflamm Regen. 2022 Oct 4;42(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s41232-022-00226-6. Inflamm Regen. 2022. PMID: 36192814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Derivatives of Natural Chlorophylls as Agents for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6392. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126392. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

