Protective effect of troxerutin and cerebroprotein hydrolysate injection on cerebral ischemia through inhibition of oxidative stress and promotion of angiogenesis in rats
- PMID: 30816516
- PMCID: PMC6423560
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9960
Protective effect of troxerutin and cerebroprotein hydrolysate injection on cerebral ischemia through inhibition of oxidative stress and promotion of angiogenesis in rats
Abstract
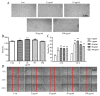
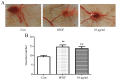
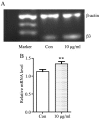
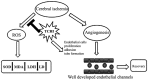
Brain ischemia, including cerebral ischemia and cerebrovascular ischemia, leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia, and causes brain tissue death or cerebral infarction/ischemic stroke. The troxerutin and cerebroprotein hydrolysate injection (TCHI), is widely applied in China to improve blood supply in ischemic brain tissues and to enhance neuroprotective effects in clinical practice. However, the benefits and detailed underlying mechanism elaborating the effectiveness of TCHI in cerebrovascular diseases require further investigation. Therefore, in the present study, experimental in vivo and in vitro models were employed to investigate the potential mechanisms of TCHI on cerebral ischemic injury. The results demonstrated that TCHI increased the lactate dehydrogenase levels in the brain homogenate and conversely decreased lactic acid levels. TCHI was further observed to significantly increase superoxide dismutase activity and decrease malondialdehyde levels in ischemic brain tissues. In addition, TCHI significantly induced vascular maturation processes, including proliferation, adhesion, migration and tube formation in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Additionally, TCHI significantly stimulated microvessel formation in the rat aortic ring and chick chorioallantoic membrane assays. Taken together, these results provided strong evidence that TCHI stimulated angiogenesis at multiple steps, and indicated that TCHI attenuated cerebral ischemic damage through the amelioration of oxidative stress and promotion of angiogenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Troxerutin Abrogates Ischemic/Reperfusion-Induced Brain Injury through Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Neuronal Inflammation by Inhibiting the Expression of NLRP3 in Sprague Dawley Rats.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2021;40(4):11-19. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2021038860. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34936296
-
[Effect of troxerutin and cerebroproptein hydrolysate injection on platelet aggregation and thrombosis].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Feb;19(1):193-6. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21362250 Chinese.
-
Troxerutin and Cerebroprotein Hydrolysate Injection Protects Neurovascular Units from Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation-Induced Injury In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 May 2;2018:9859672. doi: 10.1155/2018/9859672. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29853981 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron protection as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke.Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(14):1317-34. doi: 10.2174/156802609789869646. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19849659 Review.
-
Experimental therapy with tissue kallikrein against cerebral ischemia.Front Biosci. 2006 May 1;11:1323-7. doi: 10.2741/1886. Front Biosci. 2006. PMID: 16368519 Review.
Cited by
-
The Protective Roles and Molecular Mechanisms of Troxerutin (Vitamin P4) for the Treatment of Chronic Diseases: A Mechanistic Review.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(1):97-110. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200510020744. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32386493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feasibility of Catalpol Intranasal Administration and Its Protective Effect on Acute Cerebral Ischemia in Rats via Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Jan 25;16:279-296. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S343928. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35115763 Free PMC article.
-
Troxerutin attenuates oxygen‑glucose deprivation and reoxygenation‑induced oxidative stress and inflammation by enhancing the PI3K/AKT/HIF‑1α signaling pathway in H9C2 cardiomyocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):1351-1361. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11207. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32626962 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Diosgenin-Amino Acid Derivatives with Dual Functions of Neuroprotection and Angiogenesis.Molecules. 2019 Nov 7;24(22):4025. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224025. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31703284 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Effects of Troxerutin and Cerebroprotein Hydrolysate Injection on Injured Spinal Cords in Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 4;2020:3561235. doi: 10.1155/2020/3561235. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Writing Group Members, Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, Ford E, Furie K, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2010 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;121:e46–e215. - PubMed
-
- Soleimannejad K, Rahmani A, Hatefi M, Khataminia M, Hafezi Ahmadi MR, Asadollahi K. Effects of nigella sativa extract on markers of cerebral angiogenesis after global ischemia of brain in rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26:1514–1520. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.02.040. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

