VIP activates primordial follicles of rat through ERK-mTOR pathway in tissue culture
- PMID: 30817320
- PMCID: PMC6433003
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-18-0466
VIP activates primordial follicles of rat through ERK-mTOR pathway in tissue culture
Abstract
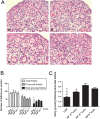
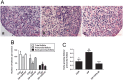
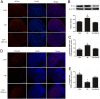
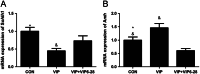
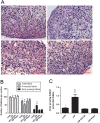
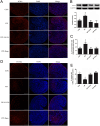
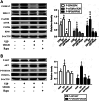
In vitro activation of primordial follicles is becoming more essential in assisted reproductive technologies. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is one of the members of the neurotrophin family which has demonstrated to have an impact on follicle development in recent years. This study aims to investigate the effect of VIP on the activation of primordial follicles in neonatal rat in an in vitro culture system and to determine the relevant molecular mechanism of their activation. Ovaries of 4-day-old rats were examined for the expression of VIP receptors and were cultured in mediums containing VIP with or without inhibitors of the ERK-mTOR signalling pathway. They were then collected for histological analysis or measurement of the molecular expression of this pathway. The receptors of VIP were found in granular cells and oocytes of primordial and early-growing follicles in neonatal ovary. The ratio of growing follicle increased in the presence VIP at different concentrations, with the highest level of increase being observed in the 10-7 mol/L VIP-treated group. The ratio of PCNA-positive granular cells was also increased, while that of the apoptotic oocytes were decreased, and protein analysis showed increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2, mTOR and RPS6 in the VIP-treated group. However, the effect of VIP on the activation of primordial follicle became insignificant with the addition of MEK inhibitor (U0126) or mTORC1 inhibitor (rapamycin). This study indicated that VIP could activate neonatal rat primordial follicle through the ERK-mTOR signalling pathway, suggesting a strategy for in vitro primordial follicle recruitment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vasoactive intestinal peptide can promote the development of neonatal rat primordial follicles during in vitro culture.Biol Reprod. 2013 Jan 17;88(1):12. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.098335. Print 2013 Jan. Biol Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23175772
-
Rapamycin preserves the primordial follicle pool during cisplatin treatment in vitro and in vivo.Mol Reprod Dev. 2020 Apr;87(4):442-453. doi: 10.1002/mrd.23330. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Mol Reprod Dev. 2020. PMID: 32112509
-
MAPK3/1 participates in the activation of primordial follicles through mTORC1-KITL signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;233(1):226-237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25868. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28218391
-
Cellular and molecular regulation of the activation of mammalian primordial follicles: somatic cells initiate follicle activation in adulthood.Hum Reprod Update. 2015 Nov-Dec;21(6):779-86. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv037. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Hum Reprod Update. 2015. PMID: 26231759 Review.
-
Regulation of primordial follicle formation, dormancy, and activation in mice.J Reprod Dev. 2021 Jun 21;67(3):189-195. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2021-040. Epub 2021 Apr 25. J Reprod Dev. 2021. PMID: 33896884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The roles of MAPK signaling pathway in ovarian folliculogenesis.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jul 14;18(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01737-9. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40660328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-378d is Involved in the Regulation of Apoptosis and Autophagy of and E2 Secretion from Cultured Ovarian Granular Cells Treated by Sodium Fluoride.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Nov;199(11):4119-4128. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02524-x. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 33405077
-
Folic acid Ameliorates the Declining Quality of Sodium Fluoride-Exposed Mouse Oocytes through the Sirt1/Sod2 Pathway.Aging Dis. 2022 Oct 1;13(5):1471-1487. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0217. eCollection 2022 Oct 1. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 36186127 Free PMC article.
-
Making a good egg: human oocyte health, aging, and in vitro development.Physiol Rev. 2023 Oct 1;103(4):2623-2677. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00032.2022. Epub 2023 May 12. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37171807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide variation study and inter-tissue communication analysis unveil regulatory mechanisms of egg-laying performance in chickens.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 16;15(1):7069. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50809-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39152103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barberi M, Muciaccia B, Morelli MB, Stefanini M, Cecconi S, Canipari R. 2007. Expression localization and functional activity of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and their receptors in mouse ovary. Reproduction 134 281–292. (10.1530/REP-07-0051) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bruno JB, Celestino JJ, Lima-Verde IB, Matos MH, Lima LF, Name KP, Araújo VR, Saraiva MV, Martins FS, Campello CC. et al. 2010. Vasoactive intestinal peptide improves the survival and development of caprine preantral follicles after in vitro tissue culture. Cells Tissues Organs 191 414–421. (10.1159/000272317) - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

